Urban sanitation coverage and environmental fecal contamination: Links between the household and public environments of Accra, Ghana
- PMID: 29969466
- PMCID: PMC6029754
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199304
Urban sanitation coverage and environmental fecal contamination: Links between the household and public environments of Accra, Ghana
Abstract
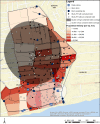
Exposure to fecal contamination in public areas, especially in dense, urban environments, may significantly contribute to enteric infection risk. This study examined associations between sanitation and fecal contamination in public environments in four low-income neighborhoods in Accra, Ghana. Soil (n = 72) and open drain (n = 90) samples were tested for E. coli, adenovirus, and norovirus. Sanitation facilities in surveyed households (n = 793) were categorized by onsite fecal sludge containment ("contained" vs. "uncontained") using previous Joint Monitoring Program infrastructure guidelines. Most sanitation facilities were shared by multiple households. Associations between spatial clustering of household sanitation coverage and fecal contamination were examined, controlling for neighborhood and population density (measured as enumeration areas in the 2010 census and spatially matched to sample locations). E. coli concentrations in drains within 50m of clusters of contained household sanitation were more than 3 log-units lower than those outside of clusters. Further, although results were not always statistically significant, E. coli concentrations in drains showed consistent trends with household sanitation coverage clusters: concentrations were lower in or near clusters of high coverage of household sanitation facilities-especially contained facilities-and vice versa. Virus detection in drains and E. coli concentrations in soil were not significantly associated with clustering of any type of household sanitation and did not exhibit consistent trends. Population density alone was not significantly associated with any of the fecal contamination outcomes by itself and was a significant, yet inconsistent, effect modifier of the association between sanitation clusters and E. coli concentrations. These findings suggest clustering of contained household sanitation, even when shared, may be associated with lower levels of fecal contamination within drains in the immediate public domain. Further research is needed to better quantify these relationships and examine impacts on health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- UNICEF, WHO. Progress on Drinking Water, Sanitation and Hygiene [Internet]. 2017. doi: 10.1111/tmi.12329 - DOI
-
- Cairncross S, Blumenthal U, Kolsky P, Moraes L, Tayeh a. The public and domestic domains in the transmission of disease. Trop Med Int Health. 1996;1: 27–34. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3156.1996.d01-9.x - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wagner EG, Lanoix JN. Excreta Disposal for Rural Areas and Small Communities. Geneva: WHO; 1958. - PubMed
-
- Labite H, Lunani I, van der Steen P, Vairavamoorthy K, Drechsel P, Lens P. Quantitative Microbial Risk Analysis to evaluate health effects of interventions in the urban water system of Accra, Ghana. J Water Health. 2010;8: 417–30. doi: 10.2166/wh.2010.021 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Katukiza AY, Ronteltap M, van der Steen P, Foppen JW a, Lens PNL. Quantification of microbial risks to human health caused by waterborne viruses and bacteria in an urban slum. J Appl Microbiol. 2013; 1–17. doi: 10.1111/jam.12368 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

