Hypertension: a new treatment for an old disease? Targeting the immune system
- PMID: 29969833
- PMCID: PMC6534786
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14436
Hypertension: a new treatment for an old disease? Targeting the immune system
Abstract
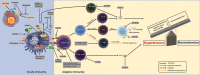
Arterial hypertension represents a serious public health problem, being a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. The availability of many antihypertensive therapeutic strategies still fails to adequately treat around 20% of hypertensive patients, who are considered resistant to conventional treatment. In the pathogenesis of hypertension, immune system mechanisms are activated and both the innate and adaptive immune responses play a crucial role. However, what, when and how the immune system is triggered during hypertension development is still largely undefined. In this context, this review highlights scientific advances in the manipulation of the immune system in order to attenuate hypertension and end-organ damage. Here, we discuss the potential use of immunosuppressants and immunomodulators as pharmacological tools to control the activation of the immune system, by non-specific and specific mechanisms, to treat hypertension and improve end-organ damage. Nevertheless, more clinical trials should be performed with these drugs to establish their therapeutic efficacy, safety and risk-benefit ratio in hypertensive conditions. LINKED ARTICLES: This article is part of a themed section on Immune Targets in Hypertension. To view the other articles in this section visit http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.v176.12/issuetoc.
© 2018 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abbate A, Van Tassell BW, Biondi‐Zoccai G, Kontos MC, Grizzard JD, Spillman DW et al (2013). Effects of interleukin‐1 blockade with anakinra on adverse cardiac remodeling and heart failure after acute myocardial infarction [from the Virginia Commonwealth University – Anakinra Remodeling Trial (2) (VCU‐ART2) pilot study]. Am J Cardiol 111: 1394–1400. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahn KO, Lim SW, Li C, Yang HJ, Ghee JY, Kim JY et al (2007). Influence of angiotensin II on expression of toll‐like receptor 2 and maturation of dendritic cells in chronic cyclosporine nephropathy. Transplantation 83: 938–947. - PubMed
-
- Albuquerque D, Nihei J, Cardillo F, Singh R (2010). The ACE inhibitors enalapril and captopril modulate cytokine responses in Balb/c and C57Bl/6 normal mice and increase CD4+CD103+CD25negative splenic T cell numbers. Cell Immunol 260: 92–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

