Nm23-H1 is involved in the repair of ionizing radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in the A549 lung cancer cell line
- PMID: 29970055
- PMCID: PMC6029351
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4592-2
Nm23-H1 is involved in the repair of ionizing radiation-induced DNA double-strand breaks in the A549 lung cancer cell line
Abstract
Background: Although originally identified as a putative metastasis suppressor, increasing studies have confirmed a possible role for Nm23-H1 in DNA repair, through the base excision repair and nucleotide excision repair pathways. In this study, we explored whether Nm23-H1 was also involved in double-strand break repair (DSBR).
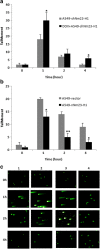
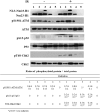
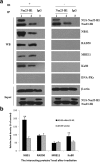
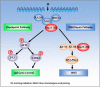
Methods and results: We constructed a stable A549-shNm23-H1 cell line with doxycycline-regulated expression of Nm23-H1, and a A549-nNm23-H1 cell line that over expressed a nucleus-localized version of Nm23-H1. Results from both lines confirmed that Nm23-H1 participated in the repair of double-strand breaks induced by X-rays, using Comet and γ-H2AX foci assays. Subsequent studies showed that Nm23-H1 activated the phosphorylation of checkpoint-related proteins including ATM serine/threonine kinase (on S1981), tumor protein p53 (on S15), and checkpoint kinase 2 (Chk2) (on T68). We also detected interactions between Nm23-H1 and the MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 (MRN) complex, as well as Ku80. Moreover, NBS1 and Ku80 levels were comparably higher in Nm23-H1 overexpressing cells than in control cells (t = 14.462, p < 0.001 and t = 5.347, p = 0.006, respectively). As Ku80 is the keystone of the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway, we speculate that Nm23-H1 promotes DSBR through NHEJ.
Conclusions: The results indicate that Nm23-H1 participates in multiple steps of DSBR.
Keywords: Double-strand break repair; Lung cancer; Nm23-H1.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Materials and cell lines used in this study don’t require an ethical approval.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

