17p13.3 genomic rearrangement in a Chinese family with split-hand/foot malformation with long bone deficiency: report of a complicated duplication with marked variation in phenotype
- PMID: 29970136
- PMCID: PMC6029155
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-018-0838-y
17p13.3 genomic rearrangement in a Chinese family with split-hand/foot malformation with long bone deficiency: report of a complicated duplication with marked variation in phenotype
Abstract
Background: Split hand/foot malformation (SHFM) is a genetically heterogeneous limb malformation with variable expressivity. SHFM with tibia or femur aplasia is called SHFM with long bone deficiency (SHFLD). 17p13.3 duplications containing BHLHA9 are associated with SHFLD. Cases with variable SHFLD phenotype and different 17p13.3 duplicated regions are reported. The severity of long bone defect could not be simply explained by BHLHA9 overdosage or 17p13.3 duplication.
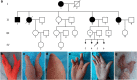
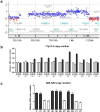
Methods: A four-generation Chinese SHFM family was recruited. Three family members have long bone defects, one male was severely affected with hypoplasia or aplasia in three of four limbs. Linkage analysis and direct sequencing of candidate genes were used to exclude six responsible genes/loci for isolated SHFM. Array comparative genomic hybridization (CGH) was performed to detect copy number variations on a genome-wide scale, and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) assays were designed to validate the identified copy number variation in the index and other family members.
Results: No mutations were found in genes or loci linked to isolated SHFM. A ~ 966 kb duplication was identified in 17p13.3 by array CGH, in which BHLHA9 surrounding region presented as triplication. The qPCR assays confirmed the indicated 17p13.3 duplication as well as BHLHA9 triplication in all available affected family members and other two asymptomatic carriers. Given the incomplete penetrance in SHFLD, those two carriers were regarded as non-penetrant, which suggested that the genomic rearrangement was co-segregated with malformation in this family.
Conclusions: The present study reports an additional SHFLD family case with 17p13.3 genomic rearrangement. To our knowledge, the 966 kb genomic rearrangement is larger in size than any previously reported SHFLD-associated 17p13.3 duplication, and the present family shows marked phenotypic variability with two asymptomatic carriers and one patient with an extremely severe phenotype. This rare case provides the opportunity to identify underlying genotype-phenotype correlations between SHFLD and 17p13.3 genomic rearrangement.
Keywords: 17p13.3 genomic rearrangement; BHLHA9; Split hand/foot malformation with long bone deficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all available individuals included in this study and the study was approved by the Ethical Review Board of Peking Union Medical College.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Naveed M, Al-Ali MT, Murthy SK, Al-Hajali S, Al-Khaja N, Deutsch S, et al. Ectrodactyly with aplasia of long bones (OMIM; 119100) in a large inbred Arab family with an apparent autosomal dominant inheritance and reduced penetrance: clinical and genetic analysis. Am J Med Genet A. 2006;140((13):1440–1446. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.31239. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Naveed M, Nath SK, Gaines M, Al-Ali MT, Al-Khaja N, Hutchings D, et al. Genomewide linkage scan for split-hand/foot malformation with long-bone deficiency in a large Arab family identifies two novel susceptibility loci on chromosomes 1q42.2-q43 and 6q14.1. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;80(1):105–111. doi: 10.1086/510724. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

