Eosinophils suppress Th1 responses and restrict bacterially induced gastrointestinal inflammation
- PMID: 29970473
- PMCID: PMC6080907
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20172049
Eosinophils suppress Th1 responses and restrict bacterially induced gastrointestinal inflammation
Abstract
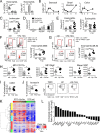
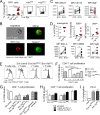
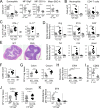
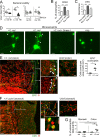
Eosinophils are predominantly known for their contribution to allergy. Here, we have examined the function and regulation of gastrointestinal eosinophils in the steady-state and during infection with Helicobacter pylori or Citrobacter rodentium We find that eosinophils are recruited to sites of infection, directly encounter live bacteria, and activate a signature transcriptional program; this applies also to human gastrointestinal eosinophils in humanized mice. The genetic or anti-IL-5-mediated depletion of eosinophils results in improved control of the infection, increased inflammation, and more pronounced Th1 responses. Eosinophils control Th1 responses via the IFN-γ-dependent up-regulation of PD-L1. Furthermore, we find that the conditional loss of IFN-γR in eosinophils phenocopies the effects of eosinophil depletion. Eosinophils further possess bactericidal properties that require their degranulation and the deployment of extracellular traps. Our results highlight two novel functions of this elusive cell type and link it to gastrointestinal homeostasis and anti-bacterial defense.
© 2018 Arnold et al.
Figures



Comment in
-
Eosinophils can more than kill.J Exp Med. 2018 Aug 6;215(8):1967-1969. doi: 10.1084/jem.20181152. Epub 2018 Jul 19. J Exp Med. 2018. PMID: 30026193 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold I.C., Zhang X., Urban S., Artola-Borán M., Manz M.G., Ottemann K.M., and Müller A.. 2017. NLRP3 Controls the Development of Gastrointestinal CD11b+ Dendritic Cells in the Steady State and during Chronic Bacterial Infection. Cell Reports. 21:3860–3872. 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.12.015 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aydemir S.A., Tekin I.O., Numanoglu G., Borazan A., and Ustundag Y.. 2004. Eosinophil infiltration, gastric juice and serum eosinophil cationic protein levels in Helicobacter pylori-associated chronic gastritis and gastric ulcer. Mediators Inflamm. 13:369–372. 10.1155/S0962935104000559 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

