Impact of ambient temperature on energy cost and economical speed during level walking in healthy young males
- PMID: 29970478
- PMCID: PMC6078347
- DOI: 10.1242/bio.035121
Impact of ambient temperature on energy cost and economical speed during level walking in healthy young males
Abstract
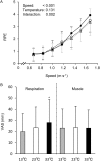
We measured oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide output during walking [per unit distance (Cw) values] for 14 healthy young human males at seven speeds from 0.67 to 1.67 m s-1 (4 min per stage) in thermoneutral (23°C), cool (13°C), and hot (33°C) environments. The Cw at faster gait speeds in the 33°C trial was slightly higher compared to those in the 23°C and 13°C trials. We found the speed at which the young males walked had a significant effect on the Cw values (P<0.05), but the different environmental temperatures showed no significant effect (P>0.05). Economical speed (ES) which can minimize the Cw in each individual was calculated from a U-shaped relationship. We found a significantly slower ES at 33°C [1.265 (0.060) m s-1 mean (s.d.)] compared to 23°C [1.349 (0.077) m s-1] and 13°C [1.356 (0.078) m s-1, P<0.05, respectively] with no differences between 23°C and 13°C (P>0.05). Heart rate and mean skin temperature responses in the 33°C condition increased throughout the walking trial compared to 23°C and 13°C (all P<0.05). These results suggest that an acutely hot environment slowed the ES by ∼7%, but an acutely cool environment did not affect the Cw and ES.
Keywords: Economical speed; Energy expenditure; Heart rate; Hot environment; Pulmonary ventilation.
© 2018. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

 (A),
(A),  (B),
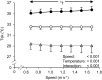
(B),  (C), and EE (D) at all gait speeds in thermoneutral (○; 23°C), cool (Δ; 13°C), and hot (●; 33°C) conditions. Values are means±standard deviation (s.d.).
(C), and EE (D) at all gait speeds in thermoneutral (○; 23°C), cool (Δ; 13°C), and hot (●; 33°C) conditions. Values are means±standard deviation (s.d.).  oxygen uptake;
oxygen uptake;  , carbon dioxide output;
, carbon dioxide output;  , pulmonary ventilation; EE, energy expenditure. *P<0.05 between 33°C and 13°C, †P<0.05 between 33°C and 23°C.
, pulmonary ventilation; EE, energy expenditure. *P<0.05 between 33°C and 13°C, †P<0.05 between 33°C and 23°C.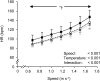
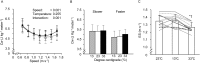
References
-
- Brouwer E. (1957). On simple formulae for calculating the heat expenditure and the quantities of carbohydrate and fat oxidized in metabolism of men and animals, from gaseous exchange (Oxygen intake and carbonic acid output) and urine-N. Acta Physiol. Pharmacol. Neerl. 6, 795-802. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

