An oxanthroquinone derivative that disrupts RAS plasma membrane localization inhibits cancer cell growth
- PMID: 29970615
- PMCID: PMC6120197
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.003907
An oxanthroquinone derivative that disrupts RAS plasma membrane localization inhibits cancer cell growth
Abstract
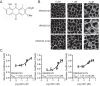
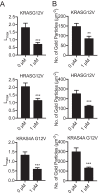
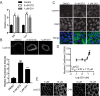
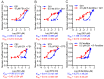
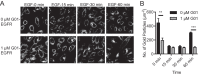
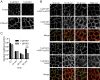
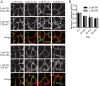
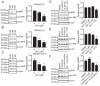
Oncogenic RAS proteins are commonly expressed in human cancer. To be functional, RAS proteins must undergo post-translational modification and localize to the plasma membrane (PM). Therefore, compounds that prevent RAS PM targeting have potential as putative RAS inhibitors. Here we examine the mechanism of action of oxanthroquinone G01 (G01), a recently described inhibitor of KRAS PM localization. We show that G01 mislocalizes HRAS and KRAS from the PM with similar potency and disrupts the spatial organization of RAS proteins remaining on the PM. G01 also inhibited recycling of epidermal growth factor receptor and transferrin receptor, but did not impair internalization of cholera toxin, indicating suppression of recycling endosome function. In searching for the mechanism of impaired endosomal recycling we observed that G01 also enhanced cellular sphingomyelin (SM) and ceramide levels and disrupted the localization of several lipid and cholesterol reporters, suggesting that the G01 molecular target may involve SM metabolism. Indeed, G01 exhibited potent synergy with other compounds that target SM metabolism in KRAS localization assays. Furthermore, G01 significantly abrogated RAS-RAF-MAPK signaling in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells expressing constitutively activated, oncogenic mutant RASG12V. G01 also inhibited the proliferation of RAS-less mouse embryo fibroblasts expressing oncogenic mutant KRASG12V or KRASG12D but not RAS-less mouse embryo fibroblasts expressing oncogenic mutant BRAFV600E. Consistent with these effects, G01 selectively inhibited the proliferation of KRAS-transformed pancreatic, colon, and endometrial cancer cells. Taken together, these results suggest that G01 should undergo further evaluation as a potential anti-RAS therapeutic.
Keywords: GTPase Kras (KRAS); Ras protein; cancer; endosome recycling; oxanthroquinone; plasma membrane; signaling; sphingolipid; sphingomyelin; trafficking.
© 2018 Tan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
Similar articles
-
Avicin G is a potent sphingomyelinase inhibitor and blocks oncogenic K- and H-Ras signaling.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 4;10(1):9120. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65882-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32499517 Free PMC article.
-
Acylpeptide hydrolase is a novel regulator of KRAS plasma membrane localization and function.J Cell Sci. 2019 Jul 31;132(15):jcs232132. doi: 10.1242/jcs.232132. J Cell Sci. 2019. PMID: 31266814 Free PMC article.
-
Fendiline inhibits K-Ras plasma membrane localization and blocks K-Ras signal transmission.Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jan;33(2):237-51. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00884-12. Epub 2012 Nov 5. Mol Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23129805 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological strategies to target oncogenic KRAS signaling in pancreatic cancer.Pharmacol Res. 2017 Mar;117:370-376. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.01.006. Epub 2017 Jan 8. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 28077300 Review.
-
Inhibitors of K-Ras plasma membrane localization.Enzymes. 2013;33 Pt A:249-65. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-416749-0.00011-7. Epub 2013 Aug 8. Enzymes. 2013. PMID: 25033808 Review.
Cited by
-
Ras Variant Biology and Contributions to Human Disease.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2262:3-18. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1190-6_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33977468 Review.
-
Structural insights, regulation, and recent advances of RAS inhibitors in the MAPK signaling cascade: a medicinal chemistry perspective.RSC Med Chem. 2025 Mar 5. doi: 10.1039/d4md00923a. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 40052089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Avicin G is a potent sphingomyelinase inhibitor and blocks oncogenic K- and H-Ras signaling.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 4;10(1):9120. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65882-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32499517 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis of key biomarkers for bladder cancer.Biomed Rep. 2022 Dec 16;18(2):14. doi: 10.3892/br.2022.1596. eCollection 2023 Feb. Biomed Rep. 2022. PMID: 36643693 Free PMC article.
-
A new ferrocene derivative blocks K-Ras localization and function by oxidative modification at His95.Life Sci Alliance. 2023 Sep 4;6(11):e202302094. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202302094. Print 2023 Nov. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 37666666 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

