Effect of Red Ginseng Extract on the Pharmacokinetics and Efficacy of Metformin in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- PMID: 29970815
- PMCID: PMC6161147
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10030080
Effect of Red Ginseng Extract on the Pharmacokinetics and Efficacy of Metformin in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
Abstract
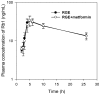
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of red ginseng extract on the pharmacokinetics (PK) and efficacy of metformin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. The diabetes mellitus rat model was established by intraperitoneally administering multiple doses of streptozotocin (30 mg/kg, twice on day 1 and 8), and diabetic rats received metformin 50 mg/kg with or without single or multiple administration of Korean red ginseng extract (RGE, 2 g/kg/day, once or for 1 week). RGE administration did not affect the plasma concentration and renal excretion of metformin. Further, diabetic rats were administered metformin (50 mg/kg) and RGE (2 g/kg) alone or concomitantly for 5 weeks, and both regimens decreased the fasting blood glucose and glycated hemoglobin (Hb-A1c) levels. Furthermore, fasting blood glucose levels were reduced by metformin or RGE administered alone but recovered to the control level following co-administration, suggesting that the effect was additive. However, triglyceride and free fatty acid levels were not different with metformin and RGE treatment alone or in combination. Biochemical parameters such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), triglycerides, total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels were not different among the three treatment groups. In conclusion, RGE and metformin showed an additive effect in glycemic control. However, the co-administration of RGE and metformin did not cause PK interactions or affect biochemical parameters including the free fatty acid, triglyceride, AST, ALT, or cholesterol levels.
Keywords: Korean red ginseng extract; diabetes; drug interaction; efficacy; metformin; pharmacokinetics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

