Recent Insights on Alzheimer's Disease Originating from Yeast Models
- PMID: 29970827
- PMCID: PMC6073265
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19071947
Recent Insights on Alzheimer's Disease Originating from Yeast Models
Abstract
In this review article, yeast model-based research advances regarding the role of Amyloid-β (Aβ), Tau and frameshift Ubiquitin UBB+1 in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) are discussed. Despite having limitations with regard to intercellular and cognitive AD aspects, these models have clearly shown their added value as complementary models for the study of the molecular aspects of these proteins, including their interplay with AD-related cellular processes such as mitochondrial dysfunction and altered proteostasis. Moreover, these yeast models have also shown their importance in translational research, e.g., in compound screenings and for AD diagnostics development. In addition to well-established Saccharomyces cerevisiae models, new upcoming Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Candida glabrata and Kluyveromyces lactis yeast models for Aβ and Tau are briefly described. Finally, traditional and more innovative research methodologies, e.g., for studying protein oligomerization/aggregation, are highlighted.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Tau; aggregation; amyloid β; oligomerization; prion; ubiquitin; yeast.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
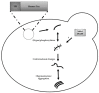
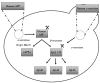
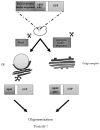
References
-
- Prince M., Guerchet M., Prina M. The Epidemiology and Impact of Dementia: Current State and Future Trends. [(accessed on 26 March 2015)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/mental_health/neurology/en/
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

