Isoflavones Production and Possible Mechanism of Their Exudation in Genista tinctoria L. Suspension Culture after Treatment with Vanadium Compounds
- PMID: 29970854
- PMCID: PMC6099964
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23071619
Isoflavones Production and Possible Mechanism of Their Exudation in Genista tinctoria L. Suspension Culture after Treatment with Vanadium Compounds
Abstract
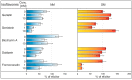
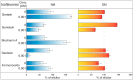
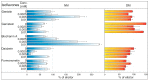
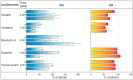
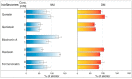
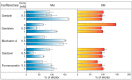
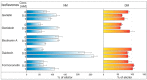
The family Fabaceae traditionally serves as a food and herbal remedies source. Certain plants serve for treatment of menopausal symptoms based on a presence of typical secondary metabolites, isoflavones. Beside soybean and clovers, other plants or cultures in vitro can produce these molecules. A cultivation in vitro can be enhanced by elicitation that stimulates metabolites biosynthesis via stress reaction. Vanadium compounds have been already described as potential elicitors, and the aim of this study was to determine the impact of NH₄VO₃ and VOSO₄ solutions on isoflavones production in Genista tinctoria L. cell cultures. The significant increase of isoflavones content, such as genistin, genistein, or formononetin, was measured in a nutrient medium or dry mass after NH₄VO₃ treatment for 24 or 48 h. The possible transport mechanism of isoflavones release as a result of elicitation was further evaluated. An incubation with different transport inhibitors prior to elicitation took effect on isoflavones content in the medium. However, there was a non-ended result for particular metabolites such as genistein and daidzein, where ATP-binding cassette (ABC) or, alternatively, multidrug and toxin extrusion (MATE) proteins can participate. Possible elicitation by some inhibitors was discussed as a result of their pleiotropic effect. Despite this outcome, the determination of the transport mechanism is an important step for identification of the specific transporter.
Keywords: Dyer’s Greenweed; elicitation; heavy metals; plasma membrane transport.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Troalen L.G., Phillips A.S., Peggie D.A., Barran P.E., Hulme A.N. Historical textile dyeing with Genista tinctoria L.: A comprehensive study by UPLC-MS/MS analysis. Anal. Methods. 2014;6:8915–8923. doi: 10.1039/C4AY01509F. - DOI
-
- Fakir H., Korkmaz M., Güller B. Medicinal plant diversity of western Mediterrenean region in Turkey. J. Appl. Biol. Sci. 2009;3:30–40.
-
- Tero-Vescan A., Vari C.E., Vlase L. Alkaloid content of some potential isoflavonoids sources (native genista species). Long-term safety implications. Farmacia. 2014;62:1109–1117.
-
- Tero-Vescan A., Imre S., Vari C.E., Oşan A., Dogaru M.T., Csedö C. Determination of some isoflavonoids and flavonoids from Genista tinctoria L. by HPLC-UV. Farmacia. 2009;57:120–127.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

