Consequences of blunting the mevalonate pathway in cancer identified by a pluri-omics approach
- PMID: 29970880
- PMCID: PMC6030166
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-018-0761-0
Consequences of blunting the mevalonate pathway in cancer identified by a pluri-omics approach
Abstract
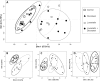
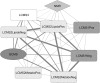
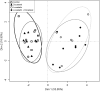
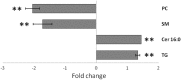
We have previously shown that the combination of statins and taxanes was a powerful trigger of HGT-1 human gastric cancer cells' apoptosis1. Importantly, several genes involved in the "Central carbon metabolism pathway in cancer", as reported in the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes, were either up- (ACLY, ERBB2, GCK, MYC, PGM, PKFB2, SLC1A5, SLC7A5, SLC16A3,) or down- (IDH, MDH1, OGDH, P53, PDK) regulated in response to the drug association. In the present study, we conducted non-targeted metabolomics and lipidomics analyses by complementary methods and cross-platform initiatives, namely mass spectrometry (GC-MS, LC-MS) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), to analyze the changes resulting from these treatments. We identified several altered biochemical pathways involved in the anabolism and disposition of amino acids, sugars, and lipids. Using the Cytoscape environment with, as an input, the identified biochemical marker changes, we distinguished the functional links between pathways. Finally, looking at the overlap between metabolomics/lipidomics and transcriptome changes, we identified correlations between gene expression modifications and changes in metabolites/lipids. Among the metabolites commonly detected by all types of platforms, glutamine was the most induced (6-7-fold), pointing to an important metabolic adaptation of cancer cells. Taken together, our results demonstrated that combining robust biochemical and molecular approaches was efficient to identify both altered metabolic pathways and overlapping gene expression alterations in human gastric cancer cells engaging into apoptosis following blunting the cholesterol synthesis pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The combination of four analytical methods to explore skeletal muscle metabolomics: Better coverage of metabolic pathways or a marketing argument?J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Jan 30;148:273-279. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.10.013. Epub 2017 Oct 18. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 29059617
-
Automated pathway and reaction prediction facilitates in silico identification of unknown metabolites in human cohort studies.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2017 Dec 15;1071:58-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.04.002. Epub 2017 Apr 4. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28479069
-
Metabolic profiling of potential lung cancer biomarkers using bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and the integrated direct infusion/ gas chromatography mass spectrometry platform.J Proteomics. 2016 Aug 11;145:197-206. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2016.05.030. Epub 2016 May 30. J Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 27255828
-
Applications of mass spectrometry-based targeted and non-targeted lipidomics.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Oct 7;504(3):576-581. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.081. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29534960 Review.
-
Metabolomics, a Powerful Tool for Agricultural Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Nov 17;17(11):1871. doi: 10.3390/ijms17111871. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27869667 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Importance of Mevalonate Pathway Lipids on the Growth and Survival of Primary and Metastatic Gastric Carcinoma Cells.Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2021 May 31;14:217-228. doi: 10.2147/CEG.S310235. eCollection 2021. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34103960 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Statin Use and Gastric Cancer: A Nested Case-Control Study Using a National Health Screening Cohort in Korea.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Dec 8;14(12):1283. doi: 10.3390/ph14121283. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34959682 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Metabolomics Study Revealed Difference in Central Carbon Metabolism between Sika Deer and Red Deer Antler.Int J Genomics. 2020 Aug 25;2020:7192896. doi: 10.1155/2020/7192896. eCollection 2020. Int J Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32908856 Free PMC article.
-
MDM2-Dependent Rewiring of Metabolomic and Lipidomic Profiles in Dedifferentiated Liposarcoma Models.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 4;12(8):2157. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082157. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32759684 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy in Clinical Metabolomics and Personalized Medicine: Current Challenges and Perspectives.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Sep 20;8:698337. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.698337. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34616770 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

