Unintended effects of a targeted maternal and child nutrition intervention on household expenditures, labor income, and the nutritional status of non-targeted siblings in Ghana
- PMID: 29970953
- PMCID: PMC5917415
- DOI: 10.1016/j.worlddev.2018.02.025
Unintended effects of a targeted maternal and child nutrition intervention on household expenditures, labor income, and the nutritional status of non-targeted siblings in Ghana
Abstract
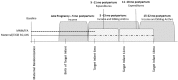
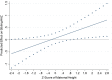
It is common for health and nutrition interventions to target specific household members and for evaluations of their effects to focus exclusively on those members. However, if a targeted intervention changes a household's utility maximization problem or influences decision-making, households might respond to the intervention in unintended ways with the potential to affect the wellbeing of non-targeted members. Using panel data from a randomized controlled nutrition trial in Ghana, we evaluate household behavioral responses to the provision of small-quantity lipid-based nutrient supplements (SQ-LNS) to mothers and their infants to prevent undernutrition. We find that targeted supplementation with SQ-LNS had a positive effect on household expenditures on food, including some nutrient-rich food groups, as well as on non-food goods and services. We also find a positive impact on labor income, particularly among fathers. We then explore intrahousehold spillover effects on the nutritional status of non-targeted young children in the household. We find evidence that the targeted provision of SQ-LNS led to higher height-for-age z-scores among non-targeted children in the LNS group compared to the non-LNS group, though only among those with relatively taller mothers, which is an indicator of a child's growth potential. These findings support existing evidence and suggest that unintended behavioral responses and spillover are a real possibility in the context of nutrition interventions targeting nutritionally-vulnerable household members. Thoughtfully considering this possibility in the design, analyses, and evaluation of targeted nutrition interventions may provide a more complete picture of overall effects.
Keywords: Child nutrition; Expenditures; Income; Intrahousehold spillovers; Randomized trial.
Figures
References
-
- Adair L.S. Filipino children exhibit catch-up growth from age 2 to 12 years. The Journal of Nutrition. 1999;129(6):1140–1148. - PubMed
-
- Adu-Afarwuah S., Lartey A., Okronipa H., Ashorn P., Peerson J.M., Arimond M.…Dewey K.G. Small-quantity, lipid-based nutrient supplements provided to women during pregnancy and 6 mo postpartum and to their infants from 6 mo of age increase the mean attained length of 18-mo-old children in semi-urban Ghana: A randomized controlled trial. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2016;104(3):797–808. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
