Bevacizumab Diminishes Inflammation in an Acute Endotoxin-Induced Uveitis Model
- PMID: 29971005
- PMCID: PMC6018210
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00649
Bevacizumab Diminishes Inflammation in an Acute Endotoxin-Induced Uveitis Model
Abstract
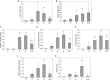
Introduction: Uveitis is an eye disease characterized by inflammation of the uvea and an early and exhaustive diagnosis is essential for its treatment. The aim of our study is to assess the potential toxicity and anti-inflammatory efficacy of Bevacizumab in an experimental uveitis model by subcutaneously injecting lipopolysaccharide into Lewis rats and to clarify its mechanism. Material and Methods: Blood-aqueous barrier integrity was assessed 24 h after endotoxin-induced uveitis (EIU) by analyzing two parameters: cell count and protein concentration in aqueous humors. Histopathology of all eye structures was also studied. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent analyses of the aqueous humor samples were performed in order to calculate the diverse chemokine and cytokine protein levels and oxidative stress-related markers were also evaluated. Results: The aqueous humor's cellular content significantly increased in the group treated with only Bevacizumab, but it had no effect on retina histopathological grading. Nevertheless, the inflammation noted in ocular structures when administering Bevacizumab with endotoxin was mostly prevented since aqueous humor cell content considerably lowered, and concomitantly with a sharp drop in uveal, vitreous, and retina histopathological grading. The values of the multi-faceted cytokine IL-2 also significantly decreased (p < 0.05 vs. endotoxin group), and the protective IL-6 and IL-10 cytokines values rose with related anti-oxidant system recovery (p < 0.05 vs. endotoxin group). Concurrently, some related M1 macrophage chemokines substantially increased, e.g., GRO/KC, a chemokine that also displays any kind of protective role. Conclusion: All these results revealed that 24 h after being administered, Bevacizumab treatment in EIU significantly prevented inflammation in various eye structures and correct results in efficacy vs. toxicity balance were obtained.
Keywords: bevacizumab; chemokines; cytokines; endotoxin-induced uveitis; inflammation; oxidative stress.
Figures

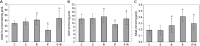


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

