Microenvironment and tumor cells: two targets for new molecular therapies of hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 29971255
- PMCID: PMC6002256
- DOI: 10.21037/tgh.2018.04.05
Microenvironment and tumor cells: two targets for new molecular therapies of hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
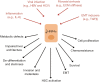
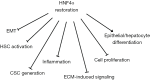
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is one of the most frequent human cancer and is characterized by a high mortality rate. The aggressiveness appears strictly related to the liver pathological background on which cancer develops. Inflammation and the consequent fibro/cirrhosis, derived from chronic injuries of several origins (viral, toxic and metabolic) and observable in almost all oncological patients, represents the most powerful risk factor for HCC and, at the same time, an important obstacle to the efficacy of systemic therapy. Multiple microenvironmental cues, indeed, play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis, evolution and recurrence of HCC as well as in the resistance to standard therapies observed in most of patients. The identification of altered pathways in cancer cells and of microenvironmental changes, strictly connected in pathogenic feedback loop, may permit to plan new therapeutic approaches targeting tumor cells and their permissive microenvironment, simultaneously.
Keywords: Hepatitis; hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF4α); liver fibrosis; transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ); yes-associated protein (YAP).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
