Targeting the mitochondrial VDAC in hepatocellular carcinoma using a polyclonal antibody-conjugated to a nitrosyl ruthenium complex
- PMID: 29971501
- PMCID: PMC6091522
- DOI: 10.1007/s00775-018-1589-x
Targeting the mitochondrial VDAC in hepatocellular carcinoma using a polyclonal antibody-conjugated to a nitrosyl ruthenium complex
Abstract
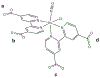
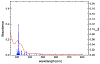
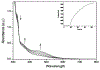
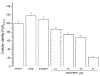
The rational design of anti-cancer agents includes a new approach based on ruthenium complexes that can act as nitric oxide (NO) donor agents against specific cellular targets. One of the most studied classes of those compounds is based on bis(bipyridine) ruthenium fragment and its derivative species. In this work, we present the chemical and cytotoxicity properties against the liver hepatocellular carcinoma cell line HepG2 of cis-[RuII(NO+)Cl(dcbpy)2]2- conjugated to a polyclonal antibody IgG (anti-VDAC) recognizing a cell surface marker. UV-visible bands of the ruthenium complex were assigned with the aid of density functional theory, which also allowed estimation of the structures that explain the biological effects of the ruthenium complex-IgG conjugate. The interaction of cis-[RuII(NO+)Cl(dcbpy)2]3- with mitochondria was evaluated due to the potential of these organelles as anti-cancer targets, and considering they interact with the anti-VDAC antibody. The cytotoxicity of cis-[RuII(NO+)Cl(dcbpy)2]3--anti-VDAC antibody was up to 80% greater in comparison to the free cis-[RuII(NO+)Cl(dcbpy)2]3- complex. We suggest that this effect is due to site-specific interaction of the complex followed by NO release.
Keywords: Conjugated ruthenium-antibody complex; Nitric oxide delivery agent; Nitrosyl ruthenium complexes.
Figures
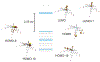
References
-
- Bonavida B (ed) (2010) Nitric oxide (NO) and cancer: prognosis, prevention, and therapy. Springer Science and Business Media, New York
-
- Serafim RA, Primi MC, Trossini GH, Ferreira EI (2012) Nitric oxide: state of the art in drug design. Curr Med Chem 19(3):386–405 - PubMed
-
- Tfouni E, Truzzi DR, Tavares A, Gomes AJ, Figueiredo LE, Franco DW (2012) Biological activity of ruthenium nitrosyl complexes. Nitric Oxide 26(1):38–53 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

