Hip and spine bone mineral density are greater in master sprinters, but not endurance runners compared with non-athletic controls
- PMID: 29971503
- PMCID: PMC6028830
- DOI: 10.1007/s11657-018-0486-9
Hip and spine bone mineral density are greater in master sprinters, but not endurance runners compared with non-athletic controls
Abstract
We examined bone density in older athletes and controls. Sprinters had greater hip and spine bone density than endurance athletes and controls, whereas values were similar in the latter two groups. These results could not be explained by differences in impact, muscle size or power between sprint and endurance athletes.
Purpose: We examined the relationship between prolonged participation in regular sprint or endurance running and skeletal health at key clinical sites in older age, and the factors responsible for any associations which we observed.
Methods: We recruited 38 master sprint runners (28 males, 10 females, mean age 71 ± 7 years), 149 master endurance runners (111 males, 38 females, mean age 70 ± 6 years) and 59 non-athletic controls (29 males, 30 females, mean age 74 ± 5 years). Dual X-ray absorptiometry was used to assess hip and spine bone mineral density (BMD), body composition (lean and fat mass), whilst jump power was assessed with jumping mechanography. In athletes, vertical impacts were recorded over 7 days from a waist-worn accelerometer, and details of starting age, age-graded performance and training hours were recorded.
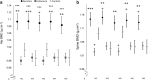
Results: In ANOVA models adjusted for sex, age, height, body composition, and jump power, sprinter hip BMD was 10 and 14% greater than that of endurance runners and controls respectively. Sprinter spine BMD was also greater than that of both endurance runners and controls. There were no differences in hip or spine BMD between endurance runners and controls. Stepwise regression showed only discipline (sprint/endurance), sex, and age as predictors of athlete spine BMD, whilst these variables and starting age were predictive of hip BMD.
Conclusions: Regular running is associated with greater BMD at the fracture-prone hip and spine sites in master sprinters but not endurance runners. These benefits cannot be explained by indicators of mechanical loading measured in this study including vertical impacts, body composition or muscular output.
Keywords: Athlete; Exercise; Mechanoadaptation; Physical activity.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Bass SL, Eser P, Daly R. The effect of exercise and nutrition on the mechanostat. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2005;5(3):239–254. - PubMed
-
- Frost HM. Bone “mass” and the “mechanostat”: a proposal. Anat Rec. 1987;219(1):1–9. - PubMed
-
- Nichols David L, Sanborn Charlotte F, Essery Eve V. Bone Density and Young Athletic Women. Sports Medicine. 2007;37(11):1001–1014. - PubMed
-
- Hannam K., Deere K. C., Hartley A., Al-Sari U. A., Clark E. M., Fraser W. D., Tobias J. H. Habitual levels of higher, but not medium or low, impact physical activity are positively related to lower limb bone strength in older women: findings from a population-based study using accelerometers to classify impact magnitude. Osteoporosis International. 2016;28(10):2813–2822. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Johansson J, Nordstrom A, Nordstrom P. Objectively measured physical activity is associated with parameters of bone in 70-year-old men and women. Bone. 2015;81:72–79. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

