Cell growth potential drives ferroptosis susceptibility in rhabdomyosarcoma and myoblast cell lines
- PMID: 29971532
- PMCID: PMC11813460
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-018-2699-0
Cell growth potential drives ferroptosis susceptibility in rhabdomyosarcoma and myoblast cell lines
Abstract
Purpose: Ferroptosis is a programmed form of iron-dependent cell death caused by lipid hydroperoxide accumulation, which can be prevented by glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPx4) activity. Here we investigated the effects of ferroptosis inducers called erastin and RSL3, which act by glutathione depletion and GPx4 inactivation, respectively, on muscle-derived cell lines of embryonal and alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS), and mouse normal skeletal C2C12 myoblasts.
Methods: Myogenic lines were exposed to stepwise increasing concentrations of ferroptosis inducers either alone or in combination with iron supplementation, iron chelating agents (bathophenanthrolinedisulfonic acid, BPS), antioxidant molecules (glutathione, N-acetylcysteine), lipid peroxidation inhibitors (ferrostatin-1), and chemotherapeutic agents (doxorubicin and actinomycin D). Drug susceptibility was quantified by measuring cell viability, proliferation and differentiation via neutral red assay, crystal violet assay and Giemsa staining, respectively. The detection of lipid hydroperoxide and protein levels was performed by immunofluorescence and Western blot analysis, respectively.
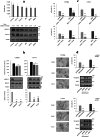
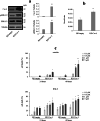
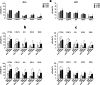
Results: Erastin and RSL3 increased lipid hydroperoxide levels preferentially in the embryonal U57810 and myoblast C2C12 lines, leading to ferroptosis that was accentuated by iron supplementation or prevented by co-treatment with BPS, glutathione, N-acetylcysteine and ferrostatin-1. The inhibition of extracellular regulated kinases (ERK) pathway prevented ferroptosis in U57810 and C2C12 cells, whereas its increased activation in the embryonal RD cells mediated by caveolin-1 (Cav-1) overexpression led to augmented ferroptosis susceptibility. Finally, we observed the combination of erastin or RSL3 with chemotherapeutic doxorubicin and actinomycin D agents to be effective in increasing cell death in all RMS lines.
Conclusions: Erastin and RSL3 trigger ferroptosis in highly proliferating myogenic lines through a ERK pathway-dependent fashion.
Keywords: Erastin; Ferroptosis; GPx4; Iron; RSL3; Rhabdomyosarcoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

