Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Combined with Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging in Differentiating Benign from Malignant Parotid Gland Lesions
- PMID: 29972148
- PMCID: PMC6064192
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.911185
Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Combined with Susceptibility-Weighted Imaging in Differentiating Benign from Malignant Parotid Gland Lesions
Abstract
BACKGROUND The aim of this study was to investigate the diagnostic value of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in combination with susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) for differentiating benign parotid gland lesions from malignant ones. MATERIAL AND METHODS This retrospective study was approved by the Ethics Committee of our hospital. A total of 36 patients (26 benign cases and 10 malignant cases) were confirmed by surgical pathology. The apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), normalized ADC (ADCNormalized), intratumoral susceptibility signals (ITSS), and morphological characteristics were analyzed with SPSS 19.0 software. RESULTS The mean ADC values of parotid gland lesions was not different between malignant and benign lesions (P=0.07), while the differences between ADCNormalized (P=0.026) and ITSS grading (P=0.014) were statistically significant. Logistic regression analysis identified use of ADCNormalized and ITSS as the only independent predictor of malignant lesions (odds ratio 0.038; 95% confidence interval 0.001~0.988; P=0.011) and (odds ratio 4.867; 95% confidence interval 1.442~16.423; P=0.049), respectively. The optimum threshold of the ADCNormalized values was -0.45%, ITSS grade was 2, the corresponding areas under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) were 0.750 and 0.787 respectively, and the combination of the 2 was 0.846. CONCLUSIONS DWI integrated with SWI can significantly improve the diagnostic efficacy in distinguishing benign from malignant parotid lesions.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
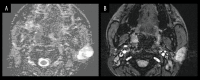
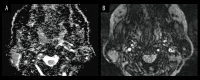
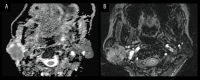
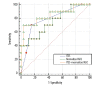
References
-
- Pinkston JA, Cole P. Incidence rates of salivary gland tumors: Results from a population-based study. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1999;120:834–40. - PubMed
-
- Freling NJ, Molenaar WM, Vermey A, et al. Malignant parotid tumors: Clinical use of MR imaging and histologic correlation. Radiology. 1992;185:691–96. - PubMed
-
- Witt RL. The significance of the margin in parotid surgery for pleomorphic adenoma. Laryngoscope. 2002;112:2141–54. - PubMed
-
- Papadogeorgakis N, Skouteris CA, Mylonas AI, Angelopoulos AP. Superficial parotidectomy: Technical modifications based on tumour characteristics. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2004;32:350–53. - PubMed
-
- Sakamoto M, Iikubo M, Kojima I, et al. Diagnostic value of capsule-like rim enhancement on magnetic resonance imaging for distinguishing malignant from benign parotid tumours. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;43:1035–41. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

