Melatonin ameliorates cognitive memory by regulation of cAMP-response element-binding protein expression and the anti-inflammatory response in a rat model of post-traumatic stress disorder
- PMID: 29973144
- PMCID: PMC6032787
- DOI: 10.1186/s12868-018-0439-7
Melatonin ameliorates cognitive memory by regulation of cAMP-response element-binding protein expression and the anti-inflammatory response in a rat model of post-traumatic stress disorder
Abstract
Background: Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is an important psychological disease that can develop following the physical experience or witnessing of traumatic events. The psychopathological response to traumatic stressors increases inflammation in the hippocampus and induces memory deficits. Melatonin (MTG) plays critical roles in circadian rhythm disorders, Alzheimer's disease, and other neurological disorders. However, the cognitive efficiency of MTG and its mechanisms of action in the treatment of PTSD remain unclear. Thus, the present study investigated the effects of MTG on spatial cognitive impairments stimulated by single prolonged stress (SPS) in rats, an animal model of PTSD. Male rats received intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of various doses of MTG for 21 consecutive days after the SPS procedure.
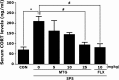
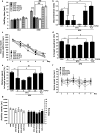
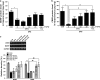
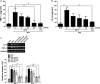
Results: SPS-stimulated cognitive impairments in the object recognition task and Morris water maze were reversed by MTG treatment (25 mg/kg, i.p). Additionally, MTG significantly increased cognitive memory-related decreases in cAMP-response element-binding (CREB) protein and mRNA levels in the hippocampus. Our results also demonstrate that MTG significantly inhibited SPS-stimulated cognitive memory impairments by inhibiting the expression of proinflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) in the rat brain.
Conclusion: The present results indicate that MTG can be beneficial for SPS-stimulated memory impairments via changes in CREB expression and proinflammatory mediators. Thus, MTG may be a prophylactic strategy for the prevention or mitigation of the progression of some features of the PTSD pathology.
Keywords: Melatonin; Memory; Post-traumatic stress disorder; Proinflammatory cytokines; cAMP-response element-binding protein.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The ethanolic extract of Aralia continentalis ameliorates cognitive deficits via modifications of BDNF expression and anti-inflammatory effects in a rat model of post-traumatic stress disorder.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Jan 8;19(1):11. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2417-0. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. PMID: 30621666 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of oleuropein on cognitive deficits and changes in hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor and cytokine expression in a rat model of post-traumatic stress disorder.J Nat Med. 2018 Jan;72(1):44-56. doi: 10.1007/s11418-017-1103-8. Epub 2017 Sep 7. J Nat Med. 2018. PMID: 28884427
-
Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate on Behavioral and Cognitive Impairments, Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Dysfunction, and Alternations in Hippocampal BDNF Expression Under Single Prolonged Stress.J Med Food. 2018 Oct;21(10):979-989. doi: 10.1089/jmf.2017.4161. Epub 2018 Sep 29. J Med Food. 2018. PMID: 30273101
-
[Cognitive impairment in post-traumatic stress disorder].Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2024;124(5):69-74. doi: 10.17116/jnevro202412405169. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2024. PMID: 38884432 Review. Russian.
-
The Potential Role of Melatonin on Memory Function: Lessons from Rodent Studies.Folia Biol (Praha). 2016;62(5):181-187. doi: 10.14712/fb2016062050181. Folia Biol (Praha). 2016. PMID: 27978412 Review.
Cited by
-
Melatonin and cannabinoids: mitochondrial-targeted molecules that may reduce inflammaging in neurodegenerative diseases.Histol Histopathol. 2020 Aug;35(8):789-800. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-212. Epub 2020 Mar 10. Histol Histopathol. 2020. PMID: 32154907 Review.
-
Post-traumatic Stress Disorder: Focus on Neuroinflammation.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Jul;60(7):3963-3978. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03320-z. Epub 2023 Apr 1. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37004607 Review.
-
Current Understanding of the Roles of Gut-Brain Axis in the Cognitive Deficits Caused by Perinatal Stress Exposure.Cells. 2023 Jun 28;12(13):1735. doi: 10.3390/cells12131735. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37443769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Asthma and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD): Emerging links, potential models and mechanisms.Brain Behav Immun. 2021 Oct;97:275-285. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2021.06.001. Epub 2021 Jun 6. Brain Behav Immun. 2021. PMID: 34107349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Relation of serum melatonin levels to postoperative delirium in older patients undergoing major abdominal surgery.J Int Med Res. 2020 Mar;48(3):300060520910642. doi: 10.1177/0300060520910642. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32208849 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anda RF, Felitti VJ, Bremner JD, Walker JD, Whitfield C, Perry BD, Dube SR, Giles WH. The enduring effects of abuse and related adverse experiences in childhood. A convergence of evidence from neurobiology and epidemiology. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2006;256(3):174–186. doi: 10.1007/s00406-005-0624-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shafia S, Vafaei AA, Samaei SA, Bandegi AR, Rafiei A, Valadan R, Hosseini-Khah Z, Mohammadkhani R, Rashidy-Pour A. Effects of moderate treadmill exercise and fluoxetine on behavioural and cognitive deficits, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis dysfunction and alternations in hippocampal BDNF and mRNA expression of apoptosis-related proteins in a rat model of post-traumatic stress disorder. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2017;139(1):165–178. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2017.01.009. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

