Up-regulation of FGF15/19 signaling promotes hepatocellular carcinoma in the background of fatty liver
- PMID: 29973237
- PMCID: PMC6031179
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-018-0781-8
Up-regulation of FGF15/19 signaling promotes hepatocellular carcinoma in the background of fatty liver
Abstract
Background: Upregulated fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19) expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) specimens is associated with tumor progression and poor prognosis. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients are at high risk for malignant transformation into HCC.
Methods: A steatohepatitis-HCC model was established in male C57L/J mice treated with N-nitrosodiethylamine (DEN) and high-fat diet (HFD). A mouse HCC cell line (Hepa1-6) and a mouse hepatocyte line (FL83B) were used to elucidate the mechanism by free fatty acids (FFA) treatment. FGF15, the mouse orthologue of FGF19, and it receptor fibroblast growth factor receptor4 (FGFR4) as well as co-receptor β-klotho were studied. FGF19 signaling was also studied in human samples of HCC with steatohepatitis.
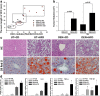
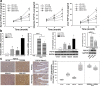
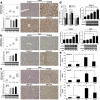
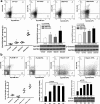
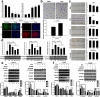
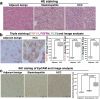
Results: HCC incidence and tumor volume were significantly increased in the DEN+HFD group compared to that in the DEN+control diet (CD) group. Increased levels of FGF15/FGFR4/β-klotho, aberrant epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and Wnt/β-catenin signaling were detected in DEN+HFD mice. Blockage of the FGF15 signal can attenuate cell migration ability and aberrant EMT and Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Conclusions: Up-regulated FGF15/FGFR4 signaling promoted the development of HCC by activation of EMT and Wnt/β-catenin signaling in the lipid metabolic disorder microenvironment. Further investigation of FGF19/FGFR4 signaling is important for potential early diagnosis and therapeutic targeting in HCC patients.
Keywords: Fibroblast growth factor 15/19; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Steatohepatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
The animal procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of University of Louisville, which is certified by the American Association for Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Miura S, Mitsuhashi N, Shimizu H, Kimura F, Yoshidome H, Otsuka M, Kato A, Shida T, Okamura D, Miyazaki M. Fibroblast growth factor 19 expression correlates with tumor progression and poorer prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:56. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-56. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

