Acupuncture as an early treatment for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSNHL) patients with flat or high-frequency drop audiograms: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 29973265
- PMCID: PMC6032598
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-018-2737-x
Acupuncture as an early treatment for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSNHL) patients with flat or high-frequency drop audiograms: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (ISSNHL) is a common form of deafness. Acupuncture has been used as a salvage therapy for ISSNHL in China since 200 BCE. However, the efficacy of acupuncture has not been confirmed in strictly controlled trials. We designed a randomized controlled clinical trial to evaluate the efficacy and long-term effects of acupuncture in patients with early ISSNHL.
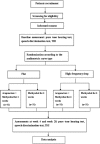
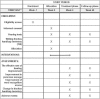
Methods/design: In this randomized controlled clinical trial, we will enroll 124 participants with ISSNHL diagnosed 2 to 4 weeks prior to enrollment, who have shown little hearing improvement after routine Western medical treatment (i.e., corticosteroids). 62 of these participants will have flat audiogram and the other 62 will have a high-frequency drop audiogram; they will all take Methycobal while half of the flat type and half of the high-frequency drop type will also receive acupuncture treatments for 4 weeks in a four-group design. The primary outcome measure will be the effective rate of hearing improvement (defined as the proportion of patients with at least 15-dB improvement in the hearing loss frequency band). The secondary outcome will measure the improvements in Pure Tone Average, Word Recognition Score, and Tinnitus Handicap Inventory. The assessments of the participants will be made at baseline, after treatment (week 4), and at follow-up (week 28).
Discussion: This study aims to explore the efficacy and long-term effects of acupuncture in patients with ISSNHL. This study will be a randomized controlled trial with strict methodology and few design deficits. If our study yields positive results, acupuncture could be recommended as a salvage therapy for patients with ISSNHL.
Trial registration: Chinese Clinical Trial Registry, ChiCTR-ICR-15006787 . Registered on 12 July 2015.
Keywords: Acupuncture; Flat; High frequency; ISSNHL; Randomized controlled trial; Study protocol.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This protocol has been approved by the Medical Ethical Committee of the Beijing Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital Affiliated with Capital Medical University. The permission number is 2014BL-063-02. Informed consent will be obtained from all participants in the trial.
Consent for publication
All authors and investigators give their consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Healthy lifestyle consultation based on traditional Chinese medicine versus routine patient education in the treatment of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss after failure of systemic therapy: study protocol for a clinical randomised trial.Trials. 2019 Dec 2;20(1):666. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3733-5. Trials. 2019. PMID: 31791370 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of Electroacupuncture and Medication for Patients With Tinnitus Associated With Idiopathic Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss: Protocol for a Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial.JMIR Res Protoc. 2025 May 14;14:e69163. doi: 10.2196/69163. JMIR Res Protoc. 2025. PMID: 40367511 Free PMC article.
-
Vestibular prognosis in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss with vestibular dysfunction treated with oral or intratympanic glucocorticoids: a protocol for randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Jul 22;21(1):669. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04579-6. Trials. 2020. PMID: 32698830 Free PMC article.
-
Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A critique on corticosteroid therapy.Hear Res. 2022 Sep 1;422:108565. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2022.108565. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Hear Res. 2022. PMID: 35816890 Review.
-
Epidemiology of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss in the era of big data.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 May;280(5):2181-2190. doi: 10.1007/s00405-022-07693-0. Epub 2022 Oct 14. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 36239782
Cited by
-
Postauricular injection in the treatment of all-frequency and high frequency descending sudden hearing loss: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Jan 22;100(3):e23847. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023847. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33545951 Free PMC article.
-
Osteopathic Cranial Manipulative Medicine as a Proposed Addition to the Treatment Regimen for Idiopathic Sudden-Onset Unilateral Sensorineural Hearing Loss: A Case Report.Cureus. 2023 Nov 30;15(11):e49728. doi: 10.7759/cureus.49728. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38161875 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of electroacupuncture for the treatment of sudden sensorineural hearing loss: A retrospective study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 May 14;100(19):e25665. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025665. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34106592 Free PMC article.
-
Intervention of the Syndrome-Position Point Selection Method on Idiopathic Tinnitus of Phlegm-Fire Stagnation Pattern: A Randomized Controlled Study.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Mar 23;2022:9664078. doi: 10.1155/2022/9664078. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 35368921 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Haberkamp TJ, Tanyeri HM, Rauch SD, Probst R, Mattox DE. Management of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Amer J Otol. 1999;20(5):587–595. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- Z141107002514069/Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission of China
- 2014-2-2232/Beijing Municipal Commission of Health and Family Plaining
- ZYLX201412/Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals Clinical Medicine Development of Special Funding Support
- 2014CB543203/National Basic Research Program of China under Grant
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous