Polymyxin B-induced skin hyperpigmentation: a rare case report and literature review
- PMID: 29973293
- PMCID: PMC6032769
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-018-0226-1
Polymyxin B-induced skin hyperpigmentation: a rare case report and literature review
Abstract
Background: Polymyxin B (PMB), which is regarded as the ultimate antibacterial treatment against some intractable gram-negative bacteria with its outstanding anti-bacterial activities, inflicts several adverse effects on patients. However, skin hyperpigmentaion (SH) induced by PMB is very rare. Here, we report a case of polymyxin B-induced skin hyperpigmentation (PMB-iSH) in a 21-year-old female. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first case of PMB-iSH in China.
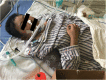
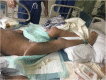
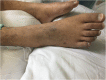
Case presentation: A 21-year-old female patient with sepsis received the administration of PMB by intravenous injection for the treatment of multi-drug resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae (MDR-KP) infection. She later suffered from a rare adverse drug reaction (ADR), namely PMB-iSH, after 5-day PMB administration during her treatment. There were multiple red rashes spread on the whole body skin at first. With the rashes fading away, SH with dark round spots appeared, associated with no pain or pruritus. The skin of the head and neck was darkened evidently, and dark brown spots were spread on the skin of trunk and limbs. About a month after her admission, urged by the relatives, the patient was transferred back to the local hospital for further treatment in the end, and her skin color didn't recover to the previous state at that time.
Conclusion: Both our case and the literature review highlight that PMB can give rise to SH indeed. Clinicians and pharmacists should attach great importance to this rare pigmentary disorder and further investigation is warranted.
Keywords: Case report; Polymyxin B; Sepsis; Skin hyperpigmentation.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by Ruijin Hospital Institutional Review Board and has been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in “Declaration of Helsinki 1964” and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. One patient was enrolled in the study and informed consent forms were signed by this patient.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient to the publication of this case report. A copy of the written informed consent is available for the review by the editor of this journal.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials