Iberian pig mesenchymal stem/stromal cells from dermal skin, abdominal and subcutaneous adipose tissues, and peripheral blood: in vitro characterization and migratory properties in inflammation
- PMID: 29973295
- PMCID: PMC6032775
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-018-0933-y
Iberian pig mesenchymal stem/stromal cells from dermal skin, abdominal and subcutaneous adipose tissues, and peripheral blood: in vitro characterization and migratory properties in inflammation
Abstract
Background: Recently, the capacity of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells (MSCs) to migrate into damaged tissues has been reported. For MSCs to be a promising tool for tissue engineering and cell and gene therapy, it is essential to know their migration ability according to their tissue of origin. However, little is known about the molecular mechanisms regulating porcine MSC chemotaxis. The aim of this study was to examine the migratory properties in an inflammatory environment of porcine MSC lines from different tissue origins: subcutaneous adipose tissue (SCA-MSCs), abdominal adipose tissue (AA-MSCs), dermal skin tissue (DS-MSCs) and peripheral blood (PB-MSCs).
Methods: SCA-MSCs, AA-MSCs, DS-MSCs and PB-MSCs were isolated and analyzed in terms of morphological features, alkaline phosphatase activity, expression of cell surface and intracellular markers of pluripotency, proliferation, in vitro chondrogenic, osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation capacities, as well as their ability to migrate in response to inflammatory cytokines.
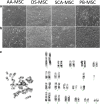
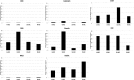
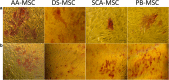
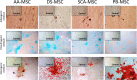
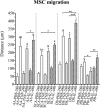
Results: SCA-MSCs, AA-MSCs, DS-MSCs and PB-MSCs were isolated and showed plastic adhesion with a fibroblast-like morphology. All MSC lines were positive for CD44, CD105, CD90 and vimentin, characteristic markers of MSCs. The cytokeratin marker was also detected in DS-MSCs. No expression of MHCII or CD34 was detected in any of the four types of MSC. In terms of pluripotency features, all MSC lines expressed POU5F1 and showed alkaline phosphatase activity. SCA-MSCs had a higher growth rate compared to the rest of the cell lines, while the AA-MSC cell line had a longer population doubling time. All MSC lines cultured under adipogenic, chondrogenic and osteogenic conditions showed differentiation capacity to the previously mentioned mesodermal lineages. All MSC lines showed migration ability in an agarose drop assay. DS-MSCs migrated greater distances than the rest of the cell lines both in nonstimulated conditions and in the presence of the inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β. SCA-MSCs and DS-MSCs increased their migration capacity in the presence of IL-1β as compared to PBS control.
Conclusions: This study describes the isolation and characterization of porcine cell lines from different tissue origin, with clear MSC properties. We show for the first time a comparative study of the migration capacity induced by inflammatory mediators of porcine MSCs of different tissue origin.
Keywords: Cell migration; Iberian pig; Inflammation; Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experimental procedures complied with the basic standards for the protection of animals used for experimental and other scientific purposes including teaching, stipulated by Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Environment. The procedures used in animals have an established Animal Use Protocol approved by the Ethics Committee Animal Experimentation at INIA. Animal manipulations were performed according to the Spanish Policy for Animal Protection RD1201/05, which meets the European Union Directive 86/609 about the protection of animals used in research. Tissue samples were taken from an Iberian boar housed in the INIA Animal Laboratory Unit (Madrid, Spain), which meets the requirements of the European Union for Scientific Procedure Establishments.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- Friedenstein AJ, Gorskaja JF, Kulagina NN. Fibroblast precursors in normal and irradiated mouse hematopoietic organs. Exp Hematol. 1976;4:267–274. - PubMed
-
- Ock SA, Baregundi Subbarao R, Lee YM, Lee JH, Jeon RH, Lee SL, et al. Comparison of immunomodulation properties of porcine mesenchymal stromal/stem cells derived from the bone marrow, adipose tissue, and dermal skin tissue. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:9581350. doi: 10.1155/2016/9581350. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

