The human naive B cell repertoire contains distinct subclasses for a germline-targeting HIV-1 vaccine immunogen
- PMID: 29973404
- PMCID: PMC6145074
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aat0381
The human naive B cell repertoire contains distinct subclasses for a germline-targeting HIV-1 vaccine immunogen
Abstract
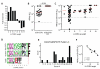
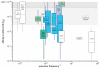
Traditional vaccine development to prevent some of the worst current pandemic diseases has been unsuccessful so far. Germline-targeting immunogens have potential to prime protective antibodies (Abs) via more targeted immune responses. Success of germline-targeting vaccines in humans will depend on the composition of the human naive B cell repertoire, including the frequencies and affinities of epitope-specific B cells. However, the human naive B cell repertoire remains largely undefined. Assessment of antigen-specific human naive B cells among hundreds of millions of B cells from multiple donors may be used as pre-phase 1 ex vivo human testing to potentially forecast B cell and Ab responses to new vaccine designs. VRC01 is an HIV broadly neutralizing Ab (bnAb) against the envelope CD4-binding site (CD4bs). We characterized naive human B cells recognizing eOD-GT8, a germline-targeting HIV-1 vaccine candidate immunogen designed to prime VRC01-class Abs. Several distinct subclasses of VRC01-class naive B cells were identified, sharing sequence characteristics with inferred precursors of known bnAbs VRC01, VRC23, PCIN63, and N6. Multiple naive B cell clones exactly matched mature VRC01-class bnAb L-CDR3 sequences. Non-VRC01-class B cells were also characterized, revealing recurrent public light chain sequences. Unexpectedly, we also identified naive B cells related to the IOMA-class CD4bs bnAb. These different subclasses within the human repertoire had strong initial affinities (KD) to the immunogen, up to 13 nM, and represent encouraging indications that multiple independent pathways may exist for vaccine-elicited VRC01-class bnAb development in most individuals. The frequencies of these distinct eOD-GT8 B cell specificities give insights into antigen-specific compositional features of the human naive B cell repertoire and provide actionable information for vaccine design and advancement.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures




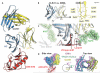
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

