Deep coverage whole genome sequences and plasma lipoprotein(a) in individuals of European and African ancestries
- PMID: 29973585
- PMCID: PMC6031652
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-04668-w
Deep coverage whole genome sequences and plasma lipoprotein(a) in individuals of European and African ancestries
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: Deep coverage whole genome sequences and plasma lipoprotein(a) in individuals of European and African ancestries.Nat Commun. 2018 Aug 23;9(1):3493. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05975-y. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30140049 Free PMC article.
-
Publisher Correction: Deep coverage whole genome sequences and plasma lipoprotein(a) in individuals of European and African ancestries.Nat Commun. 2020 Apr 1;11(1):1715. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15236-6. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32238811 Free PMC article.
Abstract
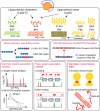
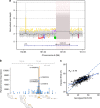
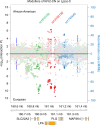
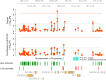
Lipoprotein(a), Lp(a), is a modified low-density lipoprotein particle that contains apolipoprotein(a), encoded by LPA, and is a highly heritable, causal risk factor for cardiovascular diseases that varies in concentrations across ancestries. Here, we use deep-coverage whole genome sequencing in 8392 individuals of European and African ancestry to discover and interpret both single-nucleotide variants and copy number (CN) variation associated with Lp(a). We observe that genetic determinants between Europeans and Africans have several unique determinants. The common variant rs12740374 associated with Lp(a) cholesterol is an eQTL for SORT1 and independent of LDL cholesterol. Observed associations of aggregates of rare non-coding variants are largely explained by LPA structural variation, namely the LPA kringle IV 2 (KIV2)-CN. Finally, we find that LPA risk genotypes confer greater relative risk for incident atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases compared to directly measured Lp(a), and are significantly associated with measures of subclinical atherosclerosis in African Americans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Tsimikas S, Hall JL. Lipoprotein(a) as a potential causal genetic risk factor of cardiovascular disease: a rationale for increased efforts to understand its pathophysiology and develop targeted therapies. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012;60:716–721. - PubMed
-
- Utermann G. The mysteries of lipoprotein(a) Science. 1989;246:904–910. - PubMed
-
- Kraft HG, Kochl S, Menzel HJ, Sandholzer C, Utermann G. The apolipoprotein (a) gene: a transcribed hypervariable locus controlling plasma lipoprotein (a) concentration. Hum. Genet. 1992;90:220–230. - PubMed
-
- Lanktree MB, Anand SS, Yusuf S, Hegele RA, Investigators S. Comprehensive analysis of genomic variation in the LPA locus and its relationship to plasma lipoprotein(a) in South Asians, Chinese, and European Caucasians. Circ. Cardiovasc Genet. 2010;3:39–46. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

