The purinergic receptor P2RX7 directs metabolic fitness of long-lived memory CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 29973721
- PMCID: PMC6054485
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-018-0282-0
The purinergic receptor P2RX7 directs metabolic fitness of long-lived memory CD8+ T cells
Abstract
Extracellular ATP (eATP) is an ancient 'danger signal' used by eukaryotes to detect cellular damage1. In mice and humans, the release of eATP during inflammation or injury stimulates both innate immune activation and chronic pain through the purinergic receptor P2RX72-4. It is unclear, however, whether this pathway influences the generation of immunological memory, a hallmark of the adaptive immune system that constitutes the basis of vaccines and protective immunity against re-infection5,6. Here we show that P2RX7 is required for the establishment, maintenance and functionality of long-lived central and tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cell populations in mice. By contrast, P2RX7 is not required for the generation of short-lived effector CD8+ T cells. Mechanistically, P2RX7 promotes mitochondrial homeostasis and metabolic function in differentiating memory CD8+ T cells, at least in part by inducing AMP-activated protein kinase. Pharmacological inhibitors of P2RX7 provoked dysregulated metabolism and differentiation of activated mouse and human CD8+ T cells in vitro, and transient P2RX7 blockade in vivo ameliorated neuropathic pain but also compromised production of CD8+ memory T cells. These findings show that activation of P2RX7 by eATP provides a common currency that both alerts the nervous and immune system to tissue damage, and promotes the metabolic fitness and survival of the most durable and functionally relevant memory CD8+ T cell populations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




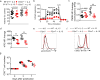
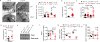


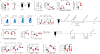

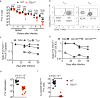



Comment in
-
P2RX7 keeps memory T cells fit.Nat Rev Immunol. 2018 Aug;18(8):482-483. doi: 10.1038/s41577-018-0041-3. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29991741 No abstract available.
-
Dangerously Fit: Extracellular ATP Aids Memory T Cell Metabolism.Immunity. 2018 Aug 21;49(2):208-210. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.08.009. Immunity. 2018. PMID: 30134200
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 AI083196/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007313/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA065493/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI075168/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL118979/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009138/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AI075168/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA157971/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DA007234/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R29 AI038903/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI038903/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL056067/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008471/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL056067/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA072669/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI038903/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

