Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 3: Emerging Role Linking Central Insulin Resistance and Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 29973864
- PMCID: PMC6020761
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00417
Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 3: Emerging Role Linking Central Insulin Resistance and Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
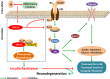
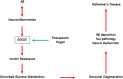
Currently, the etiology of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is still elusive. Central insulin resistance has been determined to play an important role in the progress of AD. However, the mechanism underlying the development of disrupted insulin signaling pathways in AD is unclear. Suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3) is a member of the SOCS protein family that acts as a negative modulator of insulin signaling in sensitive tissues, such as hepatocytes and adipocytes. However, little is known about its role in neurological diseases. Recent evidence indicates that the level of SOCS3 is increased in the brains of individuals with AD, especially in areas with amyloid beta deposition, suggesting that SOCS3 may regulate the central insulin signaling pathways in AD. Here, we discuss the potential role of SOCS3 in AD and speculate that SOCS3 may be a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; SOCS3; insulin resistance; neuroinflammation; therapeutic target.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

