Parallel Tests Using Culture, Xpert MTB/RIF, and SAT-TB in Sputum Plus Bronchial Alveolar Lavage Fluid Significantly Increase Diagnostic Performance of Smear-Negative Pulmonary Tuberculosis
- PMID: 29973917
- PMCID: PMC6020777
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01107
Parallel Tests Using Culture, Xpert MTB/RIF, and SAT-TB in Sputum Plus Bronchial Alveolar Lavage Fluid Significantly Increase Diagnostic Performance of Smear-Negative Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Abstract
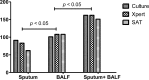
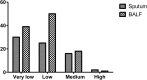
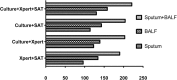
At present, tuberculosis remains a serious threat to human health. The diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB) is still difficult, and the prominent challenge for diagnosis is the lack of a highly sensitive and specific method. In order to explore the diagnostic value of parallel tests, this study prospectively enrolled 258 patients with smear-negative PTB from May 2, 2015 to December 31, 2016. The sputum specimens and bronchial alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) samples from all patients were assessed for MTB detection by culture, Xpert MTB/RIF, and simultaneous amplification and testing method for TB (SAT-TB). Overall, the sensitivity of any single test using culture, Xpert MTB/RIF, or SAT-TB was lower than that for parallel tests (p < 0.05), and the sensitivity rates for MTB detection in BALF were significantly higher than those in sputum samples. There were lower agreements in the detection results between sputum samples and BALF for all tests (p < 0.05). The parallel tests models of using culture plus Xpert MTB/RIF plus SAT-TB, culture plus Xpert, or culture plus SAT-TB achieved higher sensitivities compared with all three single test models (p < 0.05). Additionally, joint detection using sputum and BALF samples achieved a high sensitivity (0.8566, 95% CI: 0.8086-0.8941). In conclusion, the parallel tests model using culture, Xpert MTB/RIF, and SAT-TB in sputum plus BALF significantly increases the diagnostic performance of smear-negative PTB; thus, this method should be applied clinically when PTB is suspected but smear results are negative.
Keywords: SAT-TB; Xpert MTB/RIF; culture; diagnostic performance; parallel tests; pulmonary tuberculosis; smear-negative.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combined tests with Xpert MTB/RIF assay with bronchoalveolar lavage fluid increasing the diagnostic performance of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis in Eastern China.Epidemiol Infect. 2020 Dec 28;149:e5. doi: 10.1017/S095026882000309X. Epidemiol Infect. 2020. PMID: 33436140 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of SAT-TB in smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis: A diagnostic accuracy study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Dec 13;103(50):e40907. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040907. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39686443 Free PMC article.
-
[A study of the value of three molecular diagnostic techniques in the diagnosis of tuberculosis].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2015 Sep;38(9):680-5. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26703773 Chinese.
-
Systematic review: Comparison of Xpert MTB/RIF, LAMP and SAT methods for the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis.Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2016 Jan;96:75-86. doi: 10.1016/j.tube.2015.11.005. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Tuberculosis (Edinb). 2016. PMID: 26786658
-
Variation in the observed effect of Xpert MTB/RIF testing for tuberculosis on mortality: A systematic review and analysis of trial design considerations.Wellcome Open Res. 2020 Aug 17;4:173. doi: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.15412.2. eCollection 2019. Wellcome Open Res. 2020. PMID: 32851196 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Adaptation and Diagnostic Potential of a Commercial Cat Interferon Gamma Release Assay for the Detection of Mycobacterium bovis Infection in African Lions (Panthera leo).Pathogens. 2022 Jul 4;11(7):765. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11070765. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 35890010 Free PMC article.
-
The lung microbiome in HIV-positive patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis.Sci Rep. 2022 May 28;12(1):8975. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12970-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35643931 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of Laboratory Diagnosis of Tuberculosis.Clin Pract. 2024 Feb 23;14(2):388-416. doi: 10.3390/clinpract14020030. Clin Pract. 2024. PMID: 38525709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Potential Diagnostic Serum Biomarkers of Metabolomics in Osteoarticular Tuberculosis Patients: A Preliminary Study.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Mar 25;12:827528. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.827528. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35402287 Free PMC article.
-
Combined tests with Xpert MTB/RIF assay with bronchoalveolar lavage fluid increasing the diagnostic performance of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis in Eastern China.Epidemiol Infect. 2020 Dec 28;149:e5. doi: 10.1017/S095026882000309X. Epidemiol Infect. 2020. PMID: 33436140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barnard M., Warren R., Gey Van Pittius N., van Helden P., Bosman M., Streicher E., et al. (2012). Genotype MTBDRsl line probe assay shortens time to diagnosis of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis in a high-throughput diagnostic laboratory. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 186 1298–1305. 10.1164/rccm.201205-0960OC - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brent A. J., Mugo D., Musyimi R., Mutiso A., Morpeth S., Levin M., et al. (2011). Performance of the MGIT TBc identification test and meta-analysis of MPT64 assays for identification of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in liquid culture. J. Clin. Microbiol. 49 4343–4346. 10.1128/JCM.05995-11 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

