Induction of Hypergammaglobulinemia and Autoantibodies by Salmonella Infection in MyD88-Deficient Mice
- PMID: 29973931
- PMCID: PMC6019449
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01384
Induction of Hypergammaglobulinemia and Autoantibodies by Salmonella Infection in MyD88-Deficient Mice
Abstract
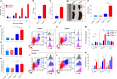
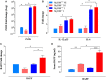
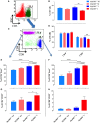
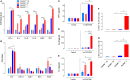
Growing evidence indicates a link between persistent infections and the development of autoimmune diseases. For instance, the inability to control Salmonella infection due to defective toll-like receptor (TLR)/myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) signaling has linked the development of persistent infections to a breakdown in B cell tolerance. However, the extent of immune dysregulation in the absence of TLR-MyD88 signaling remains poorly characterized. Here, we show that MyD88-/- mice are unable to eliminate attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium, even when challenged with a low-dose inoculum (200 CFUs/mouse), developing a persistent and progressive infection when compared to wild-type (MyD88+/+) animals. The splenic niche of MyD88-/- mice revealed increased counts of activated, Sca-1-positive, myeloid subpopulations highly expressing BAFF during persistent Salmonella infection. Likewise, the T cell compartment of Salmonella-infected MyD88-/- mice showed increased levels of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells expressing Sca-1 and CD25 and producing elevated amounts of IL-4, IL-10, and IL-21 in response to CD3/CD28 stimulation. This was associated with increased Tfh cell differentiation and the presence of CD4+ T cells co-expressing IFN-γ/IL-4 and IFN-γ/IL-10. Noteworthy, infected MyD88-/- mice had enhanced serum titers of both anti-Salmonella antibodies as well as autoantibodies directed against double-stranded DNA, thyroglobulin, and IgG rheumatoid factor, positive nuclear staining with HEp-2 cells, and immune complex deposition in the kidneys of MyD88-/- mice infected with live but not heat-killed Salmonella. Infection with other microorganisms (Acinetobacter baumanii, Streptococcus agalactiae, or Escherichia coli) was unable to trigger the autoimmune phenomenon. Our findings suggest that dysregulation of the immune response in the absence of MyD88 is pathogen-dependent and highlight potentially important genotype-environmental factor correlations.
Keywords: MyD88 deficiency; Salmonella typhiumrium; Tfh cells; autoantibodies; hypergammaglobulinemia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expansion of Tfh-like cells during chronic Salmonella exposure mediates the generation of autoimmune hypergammaglobulinemia in MyD88-deficient mice.Eur J Immunol. 2012 Mar;42(3):618-28. doi: 10.1002/eji.201141748. Epub 2011 Dec 27. Eur J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22105301
-
TLR2-, TLR4- and Myd88-independent acquired humoral and cellular immunity against Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium.Immunol Lett. 2010 Jan 4;127(2):126-34. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2009.10.008. Epub 2009 Nov 4. Immunol Lett. 2010. PMID: 19895846
-
Synergy between CD40 and MyD88 Does Not Influence Host Survival to Salmonella Infection.Front Immunol. 2015 Sep 14;6:460. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00460. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26441965 Free PMC article.
-
Differential outcome of infection with attenuated Salmonella in MyD88-deficient mice is dependent on the route of administration.Immunobiology. 2013 Jan;218(1):52-63. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2012.02.001. Epub 2012 Feb 10. Immunobiology. 2013. PMID: 22386951
-
Natural killer cell intrinsic toll-like receptor MyD88 signaling contributes to IL-12-dependent IFN-γ production by mice during infection with Toxoplasma gondii.Int J Parasitol. 2014 Jun;44(7):475-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2014.03.004. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Int J Parasitol. 2014. PMID: 24727091
Cited by
-
Pathogen Challenge and Dietary Shift Alter Microbiota Composition and Activity in a Mucin-Associated in vitro Model of the Piglet Colon (MPigut-IVM) Simulating Weaning Transition.Front Microbiol. 2021 Jul 19;12:703421. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.703421. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34349744 Free PMC article.
-
Autoimmune Diseases Following Environmental Disasters: A Narrative Review of the Literature.Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Sep 4;12(17):1767. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12171767. Healthcare (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39273791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD40L modulates transcriptional signatures of neutrophils in the bone marrow associated with development and trafficking.JCI Insight. 2021 Aug 23;6(16):e148652. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.148652. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 34255742 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between a History of Nontyphoidal Salmonella and the Risk of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Population-Based, Case-Control Study.Front Immunol. 2021 Nov 23;12:725996. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.725996. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34887848 Free PMC article.
-
GPCR-specific autoantibody signatures are associated with physiological and pathological immune homeostasis.Nat Commun. 2018 Dec 6;9(1):5224. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07598-9. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30523250 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

