Interaction of Non-Specific Lipid-Transfer Proteins With Plant-Derived Lipids and Its Impact on Allergic Sensitization
- PMID: 29973934
- PMCID: PMC6019453
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01389
Interaction of Non-Specific Lipid-Transfer Proteins With Plant-Derived Lipids and Its Impact on Allergic Sensitization
Abstract
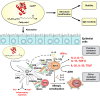
Non-specific lipid-transfer proteins (nsLTPs) represent a family of ubiquitous plant proteins belonging to the prolamin superfamily. nsLTPs are characterized by a globular α-helical structure stabilized by four disulfide bonds and a hydrophobic cavity which acts as ligand-binding site for a broad spectrum of lipids and hydrophobic molecules. nsLTPs are involved in membrane biogenesis and in the adaption of plants to abiotic and biotic stress. They display antimicrobial activity by the ability to permeabilize the cell membrane of phytopathogens. Moreover, in the presence of lipids, nsLTPs are suggested to activate the plant immune system by a receptor-dependent mechanism. Additionally, nsLTPs from pollen and plant-derived food, in particular type 1 nsLTPs (9 kDa), are described as potent allergens. Within the nsLTP family Pru p 3 from peach is the clinically most relevant allergen which can cause genuine food allergy and frequently elicits severe clinical reactions. So far, the allergenic properties of nsLTPs are attributed to both their low molecular mass and their high thermal and proteolytic stability which allow them to reach the immune system in a biological intact form. Recently, the interaction of nsLTPs with lipids has been suggested to increase their allergenic properties and to promote the allergic sensitization to these proteins. This review will summarize the current knowledge on diversity of lipid ligands of plant LTPs, and illustrate recent studies performed with allergenic nsLTPs to investigate the effect of lipid binding on the structural modification and IgE-binding properties of proteins, and finally the potential effect on the innate immune responses.
Keywords: (glycero)phospholipid; CD1d; allergen; fatty acid; invariant natural killer T cell; lipid; non-specific lipid-transfer protein.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

