Comparison between Collagen and Lidocaine Intramuscular Injections in Terms of Their Efficiency in Decreasing Myofascial Pain within Masseter Muscles: A Randomized, Single-Blind Controlled Trial
- PMID: 29973970
- PMCID: PMC6008702
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/8261090
Comparison between Collagen and Lidocaine Intramuscular Injections in Terms of Their Efficiency in Decreasing Myofascial Pain within Masseter Muscles: A Randomized, Single-Blind Controlled Trial
Abstract
Background and objective: A novel option for myofascial pain (MFP) management and muscle regeneration is intramuscular collagen injections. The aim of the study was to evaluate the efficiency of intramuscular injections of collagen and lidocaine in decreasing MFP within masseter muscles.
Methods: Myofascial pain within masseter muscles was diagnosed on the basis of the Diagnostic Criteria for Temporomandibular Disorders (II.1.A. 2 and 3). A total of 43 patients with diagnosed MFP within masseter muscles were enrolled to the study (17 male and 26 female, 40 ± 3.8 years old) and randomly divided into three groups. The first group received injections using 2 ml of collagen MD Muscle (Guna), the second group received 2 ml of 2% lidocaine without a vasoconstrictor, and the third group 2 ml of saline as a control (0.9% NaCl). All patients received repeated injections at one-week intervals (days 0 and 7). The visual analogue scale was used to determine pain intensity changes during each follow-up visit (days 0, 7, and 14) in each group. The masseter muscle activity was measured on each visit (days 0, 7, and 14) with surface electromyography (sEMG) (Neurobit Optima 4, Neurobit Systems).
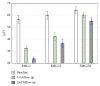
Results: We found that sEMG masseter muscle activity was significantly decreased in Group I (59.2%), less in Group II (39.3%), and least in Group III (14%). Pain intensity reduction was 53.75% in Group I, 25% in Group II, and 20.1% in Group III.
Conclusions: The study confirmed that intramuscular injection of collagen is a more efficient method for reducing myofascial pain within masseter muscles than intramuscular injection of lidocaine.
Figures

References
-
- Reissmann D. R., John M. T., Aigner A., Schön G., Sierwald I., Schiffman E. L. Interaction between awake and sleep bruxism is associated with increased presence of painful temporomandibular disorder. Journal of Oral & Facial Pain and Headache. 2017;31(4):299–305. doi: 10.11607/ofph.1885. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

