Detection of Astrovirus, Rotavirus C, and Hepatitis E Viral RNA in Adult and Juvenile Farmed Mink (Neovison vison)
- PMID: 29974054
- PMCID: PMC6020771
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2018.00132
Detection of Astrovirus, Rotavirus C, and Hepatitis E Viral RNA in Adult and Juvenile Farmed Mink (Neovison vison)
Abstract
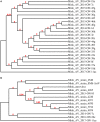
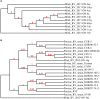
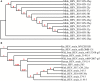
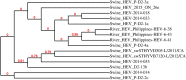
Mink astrovirus (MiAstV) is known to play a major role in mink pre-weaning diarrhea, and rotavirus and hepatitis E virus (HEV) are both considered potentially zoonotic agents. These viruses are not monitored in commercial mink, and the role of these viral infections in mink health is not well understood. This study assessed the prevalence of mink astrovirus, rotavirus C, mink HEV and swine HEV in 527 pooled healthy adult female mink and mink kit fecal samples from 50 Canadian mink farms in two seasons over 4 years. Viral RNA was extracted and amplified in RT-PCR to detect mink astrovirus and HEV RdRp genes, swine HEV ORF2, and rotavirus C VP6 gene. At least 26% of all positive samples for each virus was sequenced for phylogenetic analysis. Fourteen percent of samples were astrovirus positive, while 3 and 9% of samples were rotavirus C and mink HEV positive, respectively. One adult female sample was found to be positive by PCR for swine HEV. A significantly higher number of kit samples were astrovirus- and HEV-positive compared to adult female samples (p = 0.01 and p < 0.0001, respectively). Astrovirus was detected in significantly more summer samples from adult females compared to winter samples from adult females (p = 0.001). The detected sequences were closely related to previously reported MiAstV, swine rotavirus C, and mink and swine HEV strains. Two astrovirus sequences were distantly related to all other detected sequences as well as previously reported MiAstVs. These results demonstrate low to moderate prevalence of the three viruses in feces from clinically healthy Canadian commercial mink, and suggest that further monitoring of these viruses may provide a better understanding of how these potentially zoonotic agents may play a role in mink enteritis and overall productivity.
Keywords: astrovirus; commercial mink; fecal virus detection; hepatitis E virus; rotavirus.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

