California Autism Prevalence Trends from 1931 to 2014 and Comparison to National ASD Data from IDEA and ADDM
- PMID: 29974300
- PMCID: PMC6223814
- DOI: 10.1007/s10803-018-3670-2
California Autism Prevalence Trends from 1931 to 2014 and Comparison to National ASD Data from IDEA and ADDM
Abstract
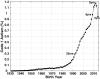
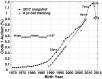
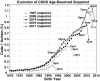
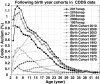
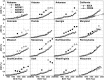
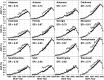
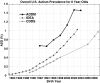
Time trends in U.S. autism prevalence from three ongoing datasets [Individuals with Disabilities Education Act, Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, and California Department of Developmental Services (CDDS)] are calculated using two different methods: (1) constant-age tracking of 8 year-olds and (2) age-resolved snapshots. The data are consistent across methods in showing a strong upward trend over time. The prevalence of autism in the CDDS dataset, the longest of the three data records, increased from 0.001% in the cohort born in 1931 to 1.2% among 5 year-olds born in 2012. This increase began around ~ 1940 at a rate that has gradually accelerated over time, including notable change points around birth years 1980, 1990 and, most recently, 2007.
Keywords: ADDM; ASD prevalence; Autism spectrum disorder; Autistic disorder; CDDS; IDEA; Time trends.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
CN, MB and WZ declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Ethics Approval
The ASD counts used in this study involved datasets in which all relevant personal information had been de-identified prior to our activities and in which the data were aggregated by age at the state level. This project therefore did not require institutional review and approval.
Figures
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 3. Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Association; 1980.
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4. Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5. Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
-
- Autism Society San Francisco Bay Area. (2015). Autism rising: A report on the increasing autism rates in California.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

