Daily walking is effective for the management of pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 29974564
- PMCID: PMC6174974
- DOI: 10.1111/jog.13698
Daily walking is effective for the management of pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus
Abstract
Aim: This study evaluated the usefulness of daily walking for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) management by analyzing the relationship between daily walking and glucose tolerance in pregnant women with GDM who were in the second trimester.
Methods: This longitudinal study was conducted at TOYOTA Memorial Hospital in Toyota, Japan, from January 2015 to June 2016. Pregnant women with GDM wore accelerometers on the waist for 7-12 weeks.
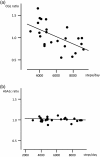
Results: Seventy-three women with GDM were included in the present study; data collected from 24 women were analyzed. The estimated number of steps walked daily showed a significant positive correlation (r = 0.798, P = 0.000) with energy expenditure related to physical activity. There was a significant negative correlation (r = -0.603, P = 0.014) between the post- to pre-research casual glucose level (CGL) ratio and the number of steps walked daily. No significant correlation (r = -0.004, P = 0.986) was detected between the ratio of hemoglobin A1c and the number of steps taken. When the study was completed, the 11 participants who walked ≥6000 steps/day showed significantly lower CGL (95 + 10 mg/dL [mean + SD]) than the 13 participants in the <6000 steps/day group (111 + 18 mg/dL) (P = 0.013).
Conclusion: Simple walking for light intensity physical activity is effective for controlling the CGL in pregnant women with GDM. We recommend that pregnant women with GDM should walk a minimum of 6000 steps/day.
Keywords: casual glucose level; daily walking; gestational diabetes mellitus; physical activity.
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Figures

References
-
- HAPO Study Cooperative Research Group , Metzger BE, Lowe LP, Dyer AR et al Hyperglycemia and adverse pregnancy outcomes. N Engl J Med 2008; 358: 1991–2002. - PubMed
-
- Morikawa M, Yamada T, Yamada T et al Change in the number of patients after the adoption of IADPSG criteria for hyperglycemia during pregnancy in Japanese women. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2010; 90: 339–342. - PubMed
-
- Fuhrmann K, Reiher H, Semmler K, Fischer F, Fischer M, Glöckner E. Prevention of congenital malformations in infants of insulin‐dependent diabetic mothers. Diabetes Care 1983; 6: 219–223. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

