Food Sources of Sodium in Korean Americans With Type 2 Diabetes: Implications for Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 29974818
- PMCID: PMC6312756
- DOI: 10.1177/1043659618785226
Food Sources of Sodium in Korean Americans With Type 2 Diabetes: Implications for Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
Introduction: Excess sodium intake can increase the risk of high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease, common comorbidities for those with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The purpose of this study is to describe sodium intake and high sodium food sources among Korean Americans (KAs) with T2DM.
Method: This study, a descriptive, secondary analysis of baseline data from a clinical trial for diabetes, recruited KAs with T2DM ( n = 232) from the community.
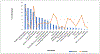
Results: Average dietary sodium intake was 3,433 mg. Major sources of dietary sodium were from bicultural diets: noodles and dumplings, Korean-style soups, kimchi, breads and snacks, and boiled or seasoned vegetables. Participants who consumed excessive sodium were more likely to consume more calories and be male, married, and more recently diagnosed with T2DM.
Discussion: High consumption of sodium among KAs with T2DM supports the need to develop effective, tailored interventions addressing dietary sodium that incorporates the individual's culture.
Keywords: Korean Americans; food sources; sodium and calorie intake; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- American Diabetes Association. (2017). Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2017. Retrieved from http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/diacare/suppl/2016/12/15/40.Sup...
-
- American Heart Association. (2015). The American Heart Association’s diet and lifestyle recommendations. Retrieved from http://www.heart.org/HEARTORG/GettingHealthy/NutritionCenter/HealthyDiet...
-
- Alderman MH, Cohen H, & Madhavan S (1998). Dietary sodium intake and mortality: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES 1). Lancet, 351, 781–785. - PubMed
-
- Cross NA, Kim KK, Yu ESH, Chen EH, & Kim J (2002). Assessment of the diet quality of middle-aged and older adult Korean Americans living in Chicago. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 102, 552–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical