ZNF424 Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Proliferation in Lung Carcinoma Cells
- PMID: 29974829
- PMCID: PMC6225340
- DOI: 10.2174/1566524018666180705113642
ZNF424 Induces Apoptosis and Inhibits Proliferation in Lung Carcinoma Cells
Abstract
Background: Previously, we showed that the Zinc finger-containing transcription factor ZNF424 inhibits p21 transcription, which has been widely associated with various cancers. However, because the roles of ZNF424 in tumorigenesis have not been characterized, we correlated ZNF424 expression with tumorigenesis in lung cancer.
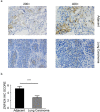
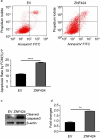
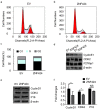
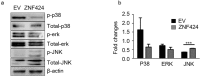
Results: The present immunohistochemical analyses show significantly lower ZNF424 expression levels in 43 of 60 lung cancer tissues compared with adjacent tissues. Moreover, flow cytometry assays indicated that overexpression of ZNF424 induces apoptosis in A549 human lung carcinoma cells, and overexpression of ZNF424 significantly increases numbers of G1 phase cells and decreases numbers of S phase cells, suggesting that ZNF424 inhibits proliferation. Western Blot analyses show that overexpression of ZNF424 decreases protein expression levels of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling proteins P-P38 and P-ERK in A549 cells.
Conclusion: These are the first data to associate ZNF424 with tumorigenesis and demonstrate an inhibitory role in lung cancer, indicating the potential of ZNF424 expression as a diagnostic marker of lung tumorigenesis.
Keywords: MAPK pathway; ZNF424; apoptosis; lung cancer..
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.org.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ZNF424, a novel human KRAB/C2H2 zinc finger protein, suppresses NFAT and p21 pathway.BMB Rep. 2010 Mar;43(3):212-8. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2010.43.3.212. BMB Rep. 2010. PMID: 20356463
-
TRIM45 Suppresses the Development of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.Curr Mol Med. 2020;20(4):299-306. doi: 10.2174/1566524019666191017143833. Curr Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 31663468
-
TRB3 interacts with ERK and JNK and contributes to the proliferation, apoptosis, and migration of lung adenocarcinoma cells.J Cell Physiol. 2020 Jan;235(1):538-547. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28993. Epub 2019 Jun 29. J Cell Physiol. 2020. PMID: 31256425
-
Low expression of Mig-6 is associated with poor survival outcome in NSCLC and inhibits cell apoptosis via ERK-mediated upregulation of Bcl-2.Oncol Rep. 2014 Apr;31(4):1707-14. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3050. Epub 2014 Feb 24. Oncol Rep. 2014. PMID: 24573418
-
ZHX2 inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of human lung cancer cells through targeting p38MAPK pathway.Cancer Biomark. 2020;27(1):75-84. doi: 10.3233/CBM-190514. Cancer Biomark. 2020. PMID: 31683461
Cited by
-
Pygo1 Regulates the Behavior of Human Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer via the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway.Dis Markers. 2022 Nov 8;2022:6993994. doi: 10.1155/2022/6993994. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 36398031 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gonzalez-Lamuno D., Loukili N., Garcia-Fuentes M., Thomson T.M. Expression and regulation of the transcriptional repressor ZNF43 in Ewing sarcoma cells. Pediatr. Pathol. Mol. Med. 2002;21(6):531–540. - PubMed
-
- Huang C., Jia Y., Yang S., et al. Characterization of ZNF23, a KRAB-containing protein that is downregulated in human cancers and inhibits cell cycle progression. Exp. Cell Res. 2007;313(2):254–263. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

