MicroRNAs Overcome Cell Fate Barrier by Reducing EZH2-Controlled REST Stability during Neuronal Conversion of Human Adult Fibroblasts
- PMID: 29974865
- PMCID: PMC6082428
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.06.007
MicroRNAs Overcome Cell Fate Barrier by Reducing EZH2-Controlled REST Stability during Neuronal Conversion of Human Adult Fibroblasts
Abstract
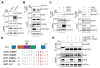
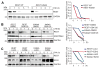
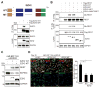
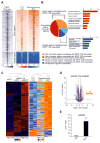
The ability to convert human somatic cells efficiently to neurons facilitates the utility of patient-derived neurons for studying neurological disorders. As such, ectopic expression of neuronal microRNAs (miRNAs), miR-9/9∗ and miR-124 (miR-9/9∗-124) in adult human fibroblasts has been found to evoke extensive reconfigurations of the chromatin and direct the fate conversion to neurons. However, how miR-9/9∗-124 break the cell fate barrier to activate the neuronal program remains to be defined. Here, we identified an anti-neurogenic function of EZH2 in fibroblasts that acts outside its role as a subunit of Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 to directly methylate and stabilize REST, a transcriptional repressor of neuronal genes. During neuronal conversion, miR-9/9∗-124 induced the repression of the EZH2-REST axis by downregulating USP14, accounting for the opening of chromatin regions harboring REST binding sites. Our findings underscore the interplay between miRNAs and protein stability cascade underlying the activation of neuronal program.
Keywords: ACTL6b; BAF complex; EZH2; REST; USP14; chromatin remodeling complex; microRNAs; neuronal reprogramming; protein modification; protein stability control.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MicroRNAs Induce a Permissive Chromatin Environment that Enables Neuronal Subtype-Specific Reprogramming of Adult Human Fibroblasts.Cell Stem Cell. 2017 Sep 7;21(3):332-348.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2017.08.002. Cell Stem Cell. 2017. PMID: 28886366 Free PMC article.
-
Polycomb complex mediated epigenetic reprogramming alters TGF-β signaling via a novel EZH2/miR-490/TGIF2 axis thereby inducing migration and EMT potential in glioblastomas.Int J Cancer. 2019 Sep 1;145(5):1254-1269. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32360. Epub 2019 May 10. Int J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31008529
-
Cross talk between microRNA and epigenetic regulation in adult neurogenesis.J Cell Biol. 2010 Apr 5;189(1):127-41. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200908151. J Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 20368621 Free PMC article.
-
From neural development to cognition: unexpected roles for chromatin.Nat Rev Genet. 2013 May;14(5):347-59. doi: 10.1038/nrg3413. Epub 2013 Apr 9. Nat Rev Genet. 2013. PMID: 23568486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNAs: regulators of neuronal fate.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013 Apr;25(2):215-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2012.12.007. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23374323 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of non-coding silencer elements and their regulation of gene expression.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Jun;24(6):383-395. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00549-9. Epub 2022 Nov 7. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36344659 Review.
-
Potentials of Cellular Reprogramming as a Novel Strategy for Neuroregeneration.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Nov 30;12:460. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00460. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30555303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CRISPR Activation Screens Systematically Identify Factors that Drive Neuronal Fate and Reprogramming.Cell Stem Cell. 2018 Nov 1;23(5):758-771.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.09.003. Epub 2018 Oct 11. Cell Stem Cell. 2018. PMID: 30318302 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecules reprogram reactive astrocytes into neuronal cells in the injured adult spinal cord.J Adv Res. 2024 May;59:111-127. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.06.013. Epub 2023 Jun 26. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 37380102 Free PMC article.
-
Post-transcriptional mechanisms controlling neurogenesis and direct neuronal reprogramming.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Sep 1;19(9):1929-1939. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.390976. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 38227517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ballas N, Grunseich C, Lu DD, Speh JC, Mandel G. REST and its corepressors mediate plasticity of neuronal gene chromatin throughout neurogenesis. Cell. 2005;121:645–57. - PubMed
-
- Battaglioli E, Andres ME, Rose DW, Chenoweth JG, Rosenfeld MG, Anderson ME, Mandel G. REST repression of neuronal genes requires components of the hSWI. SNF complex. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:41038–45. - PubMed
-
- Biggar KK, Li SS. Non-histone protein methylation as a regulator of cellular signalling and function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015;16:5–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

