Pelvic muscle floor rehabilitation as a therapeutic option in lifelong premature ejaculation: long-term outcomes
- PMID: 29974885
- PMCID: PMC6219291
- DOI: 10.4103/aja.aja_30_18
Pelvic muscle floor rehabilitation as a therapeutic option in lifelong premature ejaculation: long-term outcomes
Abstract
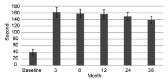
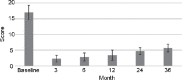
The aim of the study was to evaluate the long-term outcomes of pelvic floor muscle (PFM) rehabilitation in males with lifelong premature ejaculation (PE), using intravaginal ejaculatory latency time (IELT) and the self-report Premature Ejaculation Diagnostic Tool (PEDT) as primary outcomes. A total of 154 participants were retrospectively reviewed in this study, with 122 completing the training protocol. At baseline, all participants had an IELT ≤60 s and PEDT score >11. Participants completed a 12-week program of PFM rehabilitation, including physio-kinesiotherapy treatment, electrostimulation, and biofeedback, with three sessions per week, with 20 min for each component completed at each session. The effectiveness of intervention was evaluated by comparing the change in the geometric mean of IELT and PEDT values, from baseline, at 3, 6, and 12 months during the intervention, and at 24 and 36 months postintervention, using a paired sample 2-tailed t-test, including the associated 95% confidence intervals. Of the 122 participants who completed PFM rehabilitation, 111 gained control of their ejaculation reflex, with a mean IELT of 161.6 s and PEDT score of 2.3 at the 12-week endpoint of the intervention, representing an increase from baseline of 40.4 s and 17.0 scores, respectively, for IELT and PEDT (P < 0.0001). Of the 95 participants who completed the 36-month follow-up, 64% and 56% maintained satisfactory ejaculation control at 24 and 36 months postintervention, respectively.
Keywords: biofeedback; electrostimulation; intravaginal ejaculatory latency time; pelvic floor rehabilitation; premature ejaculation; premature ejaculation diagnostic tool.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
-
- Jannini EA, Lenzi A. Epidemiology of premature ejaculation. Curr Opin Urol. 2005;15:399–403. - PubMed
-
- La Pera G. Awareness of the role of the pelvic floor muscles in controlling the ejaculatory reflex: preliminary results. Arch Ital Urol Androl. 2012;84:74–8. - PubMed
-
- Waldinger MD, Quinn P, Dilleen M, Mundayat R, Schweitzer DH, et al. Amultinational population survey of intravaginal ejaculation latency time. J Sex Med. 2005;2:492–7. - PubMed
-
- Serefoglu EC, McMahon CG, Waldinger MD, Althof SE, Shindel A, et al. An evidence-based unified definition of lifelong and acquired premature ejaculation: report of the second international society for sexual medicine ad hoc committee for the definition of premature ejaculation. Sex Med. 2014;2:41–59. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

