Identification of a gene-expression predictor for diagnosis and personalized stratification of lupus patients
- PMID: 29975701
- PMCID: PMC6033382
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198325
Identification of a gene-expression predictor for diagnosis and personalized stratification of lupus patients
Abstract
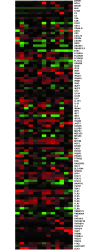
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease characterized by a wide spectrum of clinical manifestations and degrees of severity. Few genomic biomarkers for SLE have been validated and employed to inform clinical classifications and decisions. To discover and assess the gene-expression based SLE predictors in published studies, we performed a meta-analysis using our established signature database and a data similarity-driven strategy. From 13 training data sets on SLE gene-expression studies, we identified a SLE meta-signature (SLEmetaSig100) containing 100 concordant genes that are involved in DNA sensors and the IFN signaling pathway. We rigorously examined SLEmetaSig100 with both retrospective and prospective validation in two independent data sets. Using unsupervised clustering, we retrospectively elucidated that SLEmetaSig100 could classify clinical samples into two groups that correlated with SLE disease status and disease activities. More importantly, SLEmetaSig100 enabled personalized stratification demonstrating its ability to prospectively predict SLE disease at the individual patient level. To evaluate the performance of SLEmetaSig100 in predicting SLE, we predicted 1,171 testing samples to be either non-SLE or SLE with positive predictive value (97-99%), specificity (85%-84%), and sensitivity (60-84%). Our study suggests that SLEmetaSig100 has enhanced predictive value to facilitate current SLE clinical classification and provides personalized disease activity monitoring.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Agmon-Levin N, Mosca M, Petri M, Shoenfeld Y. Systemic lupus erythematosus one disease or many? Autoimmunity reviews. 2012;11(8):593–5. Epub 2011/11/02. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2011.10.020 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tsokos GC. Systemic lupus erythematosus. The New England journal of medicine. 2011;365(22):2110–21. Epub 2011/12/02. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1100359 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bombardier C, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Caron D, Chang CH. Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis and rheumatism. 1992;35(6):630–40. Epub 1992/06/01. . - PubMed
-
- Baechler EC, Batliwalla FM, Karypis G, Gaffney PM, Ortmann WA, Espe KJ, et al. Interferon-inducible gene expression signature in peripheral blood cells of patients with severe lupus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2003;100(5):2610–5. Epub 2003/02/27. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0337679100 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC151388. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bennett L, Palucka AK, Arce E, Cantrell V, Borvak J, Banchereau J, et al. Interferon and granulopoiesis signatures in systemic lupus erythematosus blood. The Journal of experimental medicine. 2003;197(6):711–23. Epub 2003/03/19. doi: 10.1084/jem.20021553 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC2193846. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

