Identification of novel susceptibility loci associated with hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B
- PMID: 29975729
- PMCID: PMC6033413
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199094
Identification of novel susceptibility loci associated with hepatitis B surface antigen seroclearance in chronic hepatitis B
Abstract
Background/aims: The seroclearance of hepatitis B virus (HBV) surface antigen (HBsAg) is regarded as a functional cure of chronic hepatitis B (CHB) although it occurs rarely. Recently, several genome-wide association studies (GWASs) revealed various genetic alterations related to the clinical course of HBV infection. However, all of these studies focused on the progression of HBV infection to chronicity and had limited application because of the heterogeneity of HBV genotypes. In the present study, we aimed to determine susceptibility genetic markers for seroclearance of HBsAg in CHB patients with a homogenous viral genotype.
Methods: One hundred patients with CHB who had experienced HBsAg seroclearance before 60 years of age and another 100 with CHB showing high serum levels of HBsAg even after 60 years of age were enrolled. Extreme-phenotype GWAS was conducted using blood samples of participants.
Results: We identified three single nucleotide polymorphisms, rs7944135 (P = 4.17 × 10-6, odds ratio [OR] = 4.16, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 2.27-7.63) at 11q12.1, rs171941 (P = 3.52×10-6, OR = 3.69, 95% CI = 2.13-6.42) at 5q14.1, and rs6462008 (P = 3.40×10-6, OR = 0.34, 95% CI = 0.22-0.54) at 7p15.2 as novel susceptibility loci associated with HBsAg seroclearance in patients with CHB. The flanking genes at these loci including MPEG1, DTX4, MTX3, and HOXA13 were suggested to have functional significance. In addition, through functional analysis, CXCL13 was also presumed to be related.
Conclusions: To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first GWAS regarding the seroclearance of HBsAg in CHB patients. We identify new susceptibility loci for cure of CHB, providing new insights into its pathophysiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

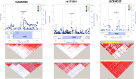

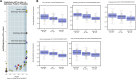
References
-
- Fattovich G, Bortolotti F, Donato F. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B: special emphasis on disease progression and prognostic factors. J Hepatol. 2008;48(2): 335–352. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2007.11.011 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ott JJ, Stevens GA, Groeger J, Wiersma ST. Global epidemiology of hepatitis B virus infection: new estimates of age-specific HBsAg seroprevalence and endemicity. Vaccine. 2012; 30(12): 2212–2219. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.12.116 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Trepo C, Chan HL, Lok A. Hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet. 2014; 384(9959): 2053–2063. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60220-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cho EJ, Kim SE, Suk KT, An J, Jeong SW, Chung WJ, et al. Current status and strategies for hepatitis B control in Korea. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2017;23(3): 205–211. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2017.0104 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chu CM, Liaw YF. HBsAg seroclearance in asymptomatic carriers of high endemic areas: appreciably high rates during a long-term follow-up. Hepatology. 2007;45(5): 1187–1192. doi: 10.1002/hep.21612 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

