Evaluation of α-tubulin, detyrosinated α-tubulin, and vimentin in CTCs: identification of the interaction between CTCs and blood cells through cytoskeletal elements
- PMID: 29976237
- PMCID: PMC6034292
- DOI: 10.1186/s13058-018-0993-z
Evaluation of α-tubulin, detyrosinated α-tubulin, and vimentin in CTCs: identification of the interaction between CTCs and blood cells through cytoskeletal elements
Abstract
Background: Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) are the major players in the metastatic process. A potential mechanism of cell migration and invasion is the formation of microtentacles in tumor cells. These structures are supported by α-tubulin (TUB), detyrosinated α-tubulin (GLU), and vimentin (VIM). In the current study, we evaluated the expression of those cytoskeletal proteins in CTCs.
Methods: Forty patients with breast cancer (BC) (16 early and 24 metastatic) were enrolled in the study. CTCs were isolated using the ISET platform and stained with the following combinations of antibodies: pancytokeratin (CK)/VIM/TUB and CK/VIM/GLU. Samples were analyzed with the ARIOL platform and confocal laser scanning microscopy.
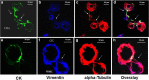
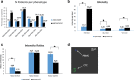
Results: Fluorescence quantification revealed that the ratios CK/TUB, CK/VIM, and CK/GLU were statistically increased in MCF7 compared with more aggressive cell lines (SKBR3 and MDA-MB-231). In addition, all of these ratios were statistically increased in MCF7 cells compared with metastatic BC patients' CTCs (p = 0.0001, p = 0.0001, and p = 0.003, respectively). Interestingly, intercellular connections among CTCs and between CTCs and blood cells through cytoskeleton bridges were revealed, whereas microtentacles were increased in patients with CTC clusters. These intercellular connections were supported by TUB, VIM, and GLU. Quantification of the examined molecules revealed that the median intensity of TUB, GLU, and VIM was significantly increased in patients with metastatic BC compared with those with early disease (TUB, 62.27 vs 11.5, p = 0.0001; GLU, 6.99 vs 5.29, p = 0.029; and VIM, 8.24 vs 5.38, p = 0.0001, respectively).
Conclusions: CTCs from patients with BC aggregate to each other and to blood cells through cytoskeletal protrusions, supported by VIM, TUB, and GLU. Quantification of these molecules could potentially identify CTCs related to more aggressive disease.
Keywords: Breast cancer; CTCs; Cytoskeleton; Detyrosinated α-tubulin; Metastasis; Microtentacles; Vimentin; α-Tubulin.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The protocol was approved by the ethics and scientific committees of our institution (D. Georgopoulos, I. Galanakis, I. Papadakis, H. Athanasakis, E. Kabitakis, M. Venihaki, A. Andreou, M. Grammatopouloou, M. Tabakaki), and all patients and healthy blood donors gave their informed consent to participate in the study.
Consent for publication
Our study does not contain any individual person’s data.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- Pantel K, Muller V, Auer M, Nusser N, Harbeck N, Braun S. Detection and clinical implications of early systemic tumor cell dissemination in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9(17):6326–6334. - PubMed
-
- Papadaki MA, Kallergi G, Zafeiriou Z, Manouras L, Theodoropoulos PA, Mavroudis D, Georgoulias V, Agelaki S. Co-expression of putative stemness and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition markers on single circulating tumour cells from patients with early and metastatic breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:651. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-651. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

