Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Induce Endothelial Cell Activation and Tissue Factor Production Through Interleukin-1α and Cathepsin G
- PMID: 29976772
- PMCID: PMC6202190
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.118.311150
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Induce Endothelial Cell Activation and Tissue Factor Production Through Interleukin-1α and Cathepsin G
Abstract
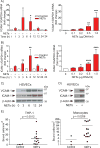
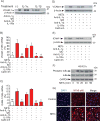
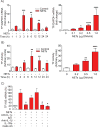
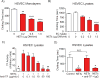
Objective- Coronary artery thrombosis can occur in the absence of plaque rupture because of superficial erosion. Erosion-prone atheromata associate with more neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) than lesions with stable or rupture-prone characteristics. The effects of NETs on endothelial cell (EC) inflammatory and thrombogenic properties remain unknown. We hypothesized that NETs alter EC functions related to erosion-associated thrombosis. Approach and Results- Exposure of human ECs to NETs increased VCAM-1 (vascular cell adhesion molecule 1) and ICAM-1 (intercellular adhesion molecule 1) mRNA and protein expression in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. THP-1 monocytoid cells and primary human monocytes bound more avidly to NET-treated human umbilical vein ECs than to unstimulated cells under flow. Treatment of human ECs with NETs augmented the expression of TF (tissue factor) mRNA, increased EC TF activity, and hastened clotting of recalcified plasma. Anti-TF-neutralizing antibody blocked NET-induced acceleration of clotting by ECs. NETs alone did not exhibit TF activity or acceleration of clotting in cell-free assays. Pretreatment of NETs with anti-interleukin (IL)-1α-neutralizing antibody or IL-1Ra (IL-1 receptor antagonist)-but not with anti-IL-1β-neutralizing antibody or control IgG-blocked NET-induced VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and TF expression. Inhibition of cathepsin G, a serine protease abundant in NETs, also limited the effect of NETs on EC activation. Cathepsin G potentiated the effect of IL-1α on ECs by cleaving the pro-IL-1α precursor and releasing the more potent mature IL-1α form. Conclusions- NETs promote EC activation and increased thrombogenicity through concerted action of IL-1α and cathepsin G. Thus, NETs may amplify and propagate EC dysfunction related to thrombosis because of superficial erosion.
Keywords: cathepsin G; endothelial cells; extracellular traps; interleukin-1; neutrophils; vascular cell adhesion molecule 1.
Figures


References
-
- Libby P. Mechanisms of acute coronary syndromes and their implications for therapy. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2004–2013. - PubMed
-
- Farb A, Burke AP, Tang AL, Liang TY, Mannan P, Smialek J, Virmani R. Coronary plaque erosion without rupture into a lipid core. A frequent cause of coronary thrombosis in sudden coronary death. Circulation. 1996;93:1354–1363. - PubMed
-
- Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Farb A, Weber DK, Kutys R, Wight TN, Virmani R. Differential accumulation of proteoglycans and hyaluronan in culprit lesions: insights into plaque erosion. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2002;22:1642–1648. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

