In Vitro Anti-Cholinesterase and Antioxidant Activity of Extracts of Moringa oleifera Plants from Rivers State, Niger Delta, Nigeria
- PMID: 29976887
- PMCID: PMC6164601
- DOI: 10.3390/medicines5030071
In Vitro Anti-Cholinesterase and Antioxidant Activity of Extracts of Moringa oleifera Plants from Rivers State, Niger Delta, Nigeria
Abstract
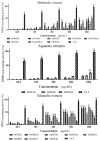
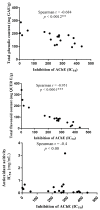
This study evaluated Moringa oleifera extracts from two locations in Niger Delta for in vitro anti-cholinesterase and antioxidant activities. Methanolic, aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Moringa oleifera were evaluated for inhibition of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity, antioxidant properties, and total phenolic and flavonoid contents using standard procedures. M. oleifera extracts possessed significant and concentration dependent AChE inhibitory activity for methanolic, aqueous, and ethanolic extracts. For the most potent extracts, the percentage AChE inhibition/IC50 (µg/mL) values were Moringa oleifera root methanolic extracts (MORME): ~80%/0.00845; Moringa oleifera root ethanolic extract 1 (MOREE1): ~90%/0.0563; Moringa oleifera root ethanolic extract 2 (MOREE2): ~70%/0.00175; and Moringa oleifera bark ethanolic extract (MOBEE): ~70%/0.0173. The descending order of AChE inhibitory potency of plant parts were: root > bark > leaf > flowers > seed. All M. oleifera methanolic extracts at a concentration of 1000 µg/mL displayed significant (p < 0.05⁻0.001) DPPH radical scavenging activity, with values of ~20⁻50% of that of ascorbic acid. The total phenolic content and total flavonoid content (TPC/TFC) of MORME, Moringa Oju bark methanolic extract (MOBME), MOREE1, MOREE2 and Moringa leaf ethanolic leaf extract (MLEE) were (287/254), (212/113), (223/185), (203/343) and (201/102) mg gallic acid equivalents/g and quercetin equivalents/g, respectively. There was an inverse correlation between plant extract AChE inhibition and total phenolic (p < 0.0001) and total flavonoid contents (p < 0.0012). In summary, this study revealed 5 of 19 extracts of M. oleifera that have potent in vitro anti-cholinesterase and antioxidant activities.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; DPPH radical scavenging; Moringa oleifera; anti-cholinesterases; antioxidant; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors can endorse that there are no conflicts of interest related with the publication of this manuscript. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An Investigation of Potential Sources of Nutraceuticals from the Niger Delta Areas, Nigeria for Attenuating Oxidative Stress.Medicines (Basel). 2019 Jan 20;6(1):15. doi: 10.3390/medicines6010015. Medicines (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30669529 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of age and extraction solvent on phytochemical content and antioxidant activity of fresh Moringa oleifera L. leaves.Food Sci Nutr. 2018 Sep 14;6(8):2188-2198. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.783. eCollection 2018 Nov. Food Sci Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30510720 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of the Crude Extracts of Moringa oleifera from Kenya and Their Correlations with Flavonoids.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Aug 9;8(8):296. doi: 10.3390/antiox8080296. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31404978 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the Safety and Efficacy of Moringa oleifera.Phytother Res. 2015 Jun;29(6):796-804. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5325. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Phytother Res. 2015. PMID: 25808883 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract on Liver Histopathology: A Systematic Review.J Nutr Metab. 2024 Jul 4;2024:6815993. doi: 10.1155/2024/6815993. eCollection 2024. J Nutr Metab. 2024. PMID: 38993633 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Cholinesterase Combination Drug Therapy as a Potential Treatment for Alzheimer's Disease.Brain Sci. 2021 Feb 2;11(2):184. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11020184. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 33540879 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant activity and calcium bioaccessibility of Moringa oleifera leaf hydrolysate, as a potential calcium supplement in food.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2020 Sep 5;29(11):1563-1571. doi: 10.1007/s10068-020-00820-9. eCollection 2020 Nov. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 33088605 Free PMC article.
-
Moringa oleifera Lam. Commercial Beverages: A Multifaceted Investigation of Consumer Perceptions, Sensory Analysis, and Bioactive Properties.Foods. 2023 Jun 2;12(11):2253. doi: 10.3390/foods12112253. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37297497 Free PMC article.
-
Moringa Oleifera Alleviates Aβ Burden and Improves Synaptic Plasticity and Cognitive Impairments in APP/PS1 Mice.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 14;14(20):4284. doi: 10.3390/nu14204284. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36296969 Free PMC article.
-
A Preliminary Assessment of the Nutraceutical Potential of Acai Berry (Euterpe sp.) as a Potential Natural Treatment for Alzheimer's Disease.Molecules. 2022 Jul 30;27(15):4891. doi: 10.3390/molecules27154891. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35956841 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rouch I., Dorey J.-M., Boublay N., Henaff M.-A., Dibie-Racoupeau F., Makaroff Z., Haston S., Benoit M., Barrellon M., Fedrico D., et al. Personality, Alzheimer’s disease and behavioural and cognitive symptoms of dementia: The PACO prospective cohort study protocol. BMC Geriatr. 2014;14:1–10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2318-14-110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Dementia. World Health Organization (WHO); Geneva, Switzerland: 2015. Fact Sheet 362.
-
- Alzheimer’s Disease International, World Alzheimer’s Report 2015: Global Impact of Dementia, 2015. [(accessed on 4 October 2016)]; Available online: http://www.alz.co.uk/research/world-report-2015.
-
- Alzheimer’s Association 2016 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2016;12:459–509. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

