Effect of Preformed or De Novo Anti-HLA Antibodies on Function and Graft Survival in Kidney Transplant Recipients
- PMID: 29976918
- PMCID: PMC6248052
- DOI: 10.12659/AOT.908491
Effect of Preformed or De Novo Anti-HLA Antibodies on Function and Graft Survival in Kidney Transplant Recipients
Abstract
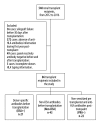
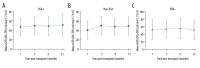
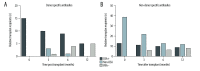
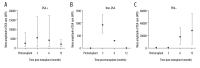
BACKGROUND Donor-specific antibodies (DSA), directed against human leucocyte antigens (HLA), are associated with increased risk for graft rejection in kidney transplantation. Anti-HLA antibodies detection by Luminex™ present high sensitivity and accuracy, but its interpretation after transplantation is not completely clear. The aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of anti-HLA antibodies, preformed or de novo, on renal function, graft survival, and incidence of antibody-mediated acute rejection (AMR). MATERIAL AND METHODS A retrospective cohort of 86 kidney transplant recipients was divided into 3 groups according to the presence of anti-HLA antibodies before transplantation: donor-specific antibodies (DSA+, n=15), non-DSA (non-DSA, n=39), and negative pre-transplant panel reactive antibodies (PRA) that became positive after transplantation (PRA-, n=22). Forty-nine recipients with negative PRA pre- and post-transplantation were excluded. Antibody specificity and intensity of fluorescence (MFI) and their relationship with renal function, proteinuria, AMR, and graft failure were evaluated. RESULTS Among patients who completed 1 year of follow-up, there was no significant difference in serum creatinine, estimated glomerular filtration rate, or proteinuria. AMR incidence was 9.5% in the DSA group, 2.3% in the non-DSA group, and 9.1% in the PRA- group. There was no correlation between fluorescence intensity and/or antibodies class (I or II) with increased risk of AMR. Thirteen grafts failed within 1 year post-transplant, there were 9 deaths due to infection, and only 1 due to AMR (PRA- group, DSA de novo at 3 months). CONCLUSIONS In contrast to previous reports, we did not find a correlation between incidence of AMR and MFI intensity in this series.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical significance of low pre-transplant donor specific antibodies (DSA) in living donor kidney recipients with negative complement-dependent cytotoxicity crossmatches (CDCXM), and negative flow cytometry crossmatches (FLXM) - A single-center experience.Transpl Immunol. 2022 Oct;74:101672. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2022.101672. Epub 2022 Jul 19. Transpl Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35868613
-
Characteristics of donor-specific anti-HLA antibodies and outcome in renal transplant patients treated with a standardized induction regimen.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017 Apr 1;32(4):730-737. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfw445. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2017. PMID: 28339671
-
Poor graft outcome in recipients with de novo donor-specific anti-HLA antibodies after living related kidney transplantation.Transpl Int. 2008 Dec;21(12):1145-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-2277.2008.00755.x. Epub 2008 Sep 17. Transpl Int. 2008. PMID: 18803618
-
[The Treatment of Acute Antibody-Mediated Rejection: Current State and Future Perspectives].G Ital Nefrol. 2024 Oct 9;41(Suppl 83):2024-S83. G Ital Nefrol. 2024. PMID: 39503229 Review. Italian.
-
The role of complement in antibody mediated transplant rejection.Mol Immunol. 2019 Aug;112:240-246. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2019.06.002. Epub 2019 Jun 10. Mol Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31195225 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Retrospective Study from a Single Center in Romania of 347 Renal Transplant Patients Treated with Tacrolimus, Mycophenolate, and Steroids to Evaluate the Association Between Anti-HLA Antibodies and 5-Year Graft Survival.Ann Transplant. 2022 Aug 12;27:e937267. doi: 10.12659/AOT.937267. Ann Transplant. 2022. PMID: 35957504 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Non-Donor-Specific HLA Antibodies on Antibody-Mediated Rejection in Pediatric Kidney Transplant Recipients.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 19;26(12):5870. doi: 10.3390/ijms26125870. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40565332 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological Results of Long-Term Use of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) Inhibitors and Its Effects on Renal Graft Functions.Ann Transplant. 2021 Sep 17;26:e932434. doi: 10.12659/AOT.932434. Ann Transplant. 2021. PMID: 34531361 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of persistent preformed and de novo donor-specific antibodies detected at 1 year after kidney transplantation on long-term graft survival in Japan: a retrospective study.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2019 Dec;23(12):1398-1406. doi: 10.1007/s10157-019-01780-z. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31493185
-
Treatment of Antibody-Mediated Rejection After Kidney Transplantation: Immunological Effects, Clinical Response, and Histological Findings.Ann Transplant. 2020 Nov 17;25:e925488. doi: 10.12659/AOT.925488. Ann Transplant. 2020. PMID: 33199675 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mackay IR, Rosen FS, Klein J, Sato A. The HLA system. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(10):702–9. - PubMed
-
- Malheiro J, Tafulo S, Dias L, et al. Analysis of preformed donor-specific anti-HLA antibodies characteristics for prediction of antibody-mediated rejection in kidney transplantation. Transpl Immunol. 2015;32(2):66–71. - PubMed
-
- Jordan SC, Vo AA. Donor-specific antibodies in allograft recipients: Etiology, impact and therapeutic approaches. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2014;19(6):591–97. - PubMed
-
- Gosset C, Lefaucheur C, Glotz D. New insights in antibody-mediated rejection. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2014;23(6):597–604. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

