α-Vinylic Amino Acids: Occurrence, Asymmetric Synthesis and Biochemical Mechanisms
- PMID: 29977107
- PMCID: PMC6029878
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tetasy.2006.02.026
α-Vinylic Amino Acids: Occurrence, Asymmetric Synthesis and Biochemical Mechanisms
Abstract
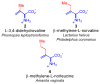
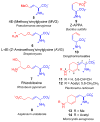
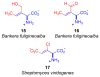
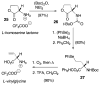
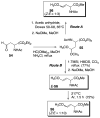
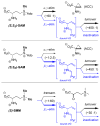
This report presents an overview of the family of naturally occurring 'vinylic' amino acids, namely those that feature a C-C double bond directly attached to the α-carbon, along the side chain. Strategies that have been brought to bear on the stereocontrolled synthesis of these olefinic amino acids are surveyed. The mechanistic diversity by which such 'vinylic triggers' can be actuated in a PLP (pyridoxal phosphate) enzyme active site is then highlighted by discussions of vinylglycine (VG), its substituted congeners, particularly AVG [4E-(2'-aminoethoxy)vinylglycine], and a naturally occurring VG-progenitor, SMM (S-methylmethionine).
Figures



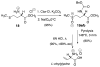








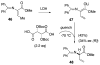

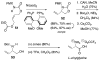



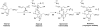

Similar articles
-
Mechanistic studies with vinylglycine and beta-haloaminobutyrates as substrates for cystathionine gamma-synthetase from Salmonella typhimurium.Biochemistry. 1979 May 1;18(9):1729-38. doi: 10.1021/bi00576a015. Biochemistry. 1979. PMID: 373802
-
Discovery and Biocatalytic Application of a PLP-Dependent Amino Acid γ-Substitution Enzyme That Catalyzes C-C Bond Formation.J Am Chem Soc. 2020 Jun 10;142(23):10506-10515. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c03535. Epub 2020 Jun 1. J Am Chem Soc. 2020. PMID: 32434326 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of ACC synthase inactivated by the mechanism-based inhibitor L-vinylglycine.FEBS Lett. 2005 Apr 25;579(11):2458-62. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2005.03.048. FEBS Lett. 2005. PMID: 15848188
-
Pyridoxal-5'-phosphate-dependent catalytic antibodies.J Immunol Methods. 2002 Nov 1;269(1-2):99-110. doi: 10.1016/s0022-1759(02)00227-2. J Immunol Methods. 2002. PMID: 12379355 Review.
-
Oxygen reactivity with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate enzymes: biochemical implications and functional relevance.Amino Acids. 2020 Aug;52(8):1089-1105. doi: 10.1007/s00726-020-02885-6. Epub 2020 Aug 25. Amino Acids. 2020. PMID: 32844248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Absence of 4-Formylaminooxyvinylglycine Production by Pseudomonas fluorescens WH6 Results in Resource Reallocation from Secondary Metabolite Production to Rhizocompetence.Microorganisms. 2021 Mar 31;9(4):717. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9040717. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 33807194 Free PMC article.
-
An Emergent Biosynthetic Pathway to Essential Amino Acids by Metabolic Metathesis.ACS Omega. 2025 May 12;10(20):20171-20178. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c10463. eCollection 2025 May 27. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 40454058 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a quaternary stereogenic center by asymmetric hydroformylation: a straightforward method to prepare chiral α-quaternary amino acids.Chem Sci. 2022 Jun 6;13(24):7215-7223. doi: 10.1039/d2sc02139k. eCollection 2022 Jun 22. Chem Sci. 2022. PMID: 35799829 Free PMC article.
-
Biomacromolecule-Assisted Screening for Reaction Discovery and Catalyst Optimization.Chem Rev. 2022 Aug 24;122(16):13800-13880. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00213. Epub 2022 Jul 29. Chem Rev. 2022. PMID: 35904776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
4-Formylaminooxyvinylglycine, an herbicidal germination-arrest factor from Pseudomonas rhizosphere bacteria.J Nat Prod. 2010 Nov 29;73(11):1853-7. doi: 10.1021/np1004856. Epub 2010 Oct 27. J Nat Prod. 2010. PMID: 20979386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eliot AC, Kirsch JF. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:383–415. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
