Effects of Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation (tVNS) on the P300 and Alpha-Amylase Level: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 29977196
- PMCID: PMC6021745
- DOI: 10.3389/fnhum.2018.00202
Effects of Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation (tVNS) on the P300 and Alpha-Amylase Level: A Pilot Study
Abstract
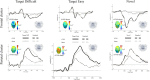
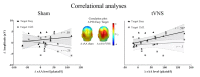
Recent research suggests that the P3b may be closely related to the activation of the locus coeruleus-norepinephrine (LC-NE) system. To further study the potential association, we applied a novel technique, the non-invasive transcutaneous vagus nerve stimulation (tVNS), which is speculated to increase noradrenaline levels. Using a within-subject cross-over design, 20 healthy participants received continuous tVNS and sham stimulation on two consecutive days (stimulation counterbalanced across participants) while performing a visual oddball task. During stimulation, oval non-targets (standard), normal-head (easy) and rotated-head (difficult) targets, as well as novel stimuli (scenes) were presented. As an indirect marker of noradrenergic activation we also collected salivary alpha-amylase (sAA) before and after stimulation. Results showed larger P3b amplitudes for target, relative to standard stimuli, irrespective of stimulation condition. Exploratory post hoc analyses, however, revealed that, in comparison to standard stimuli, easy (but not difficult) targets produced larger P3b (but not P3a) amplitudes during active tVNS, compared to sham stimulation. For sAA levels, although main analyses did not show differential effects of stimulation, direct testing revealed that tVNS (but not sham stimulation) increased sAA levels after stimulation. Additionally, larger differences between tVNS and sham stimulation in P3b magnitudes for easy targets were associated with larger increase in sAA levels after tVNS, but not after sham stimulation. Despite preliminary evidence for a modulatory influence of tVNS on the P3b, which may be partly mediated by activation of the noradrenergic system, additional research in this field is clearly warranted. Future studies need to clarify whether tVNS also facilitates other processes, such as learning and memory, and whether tVNS can be used as therapeutic tool.
Keywords: EEG; P300; locus coeruleus; norepinephrine; salivary alpha-amylase; tVNS.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

