Src Plays an Important Role in AGE-Induced Endothelial Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Tubulogenesis
- PMID: 29977209
- PMCID: PMC6021521
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2018.00765
Src Plays an Important Role in AGE-Induced Endothelial Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Tubulogenesis
Abstract
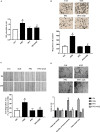
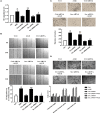
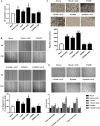
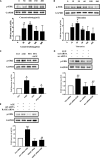
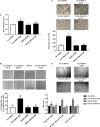
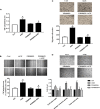
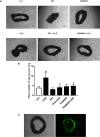
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs), produced by the non-enzymatic glycation of proteins and lipids under hyperglycemia or oxidative stress conditions, has been implicated to be pivotal in the development of diabetic vascular complications, including diabetic retinopathy. We previously demonstrated that Src kinase played a causative role in AGE-induced hyper-permeability and barrier dysfunction in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). While the increase of vascular permeability is the early event of angiogenesis, the effect of Src in AGE-induced angiogenesis and the mechanism has not been completely revealed. Here, we investigated the impact of Src on AGE-induced HUVECs proliferation, migration, and tubulogenesis. Inhibition of Src with inhibitor PP2 or siRNA decreased AGE-induced migration and tubulogenesis of HUVECs. The inactivation of Src with pcDNA3/flag-SrcK298M also restrained AGE-induced HUVECs proliferation, migration, and tube formation, while the activation of Src with pcDNA3/flag-SrcY530F enhanced HUVECs angiogenesis alone and exacerbated AGE-induced angiogenesis. AGE-enhanced HUVECs angiogenesis in vitro was accompanied with the phosphorylation of ERK in HUVECs. The inhibition of ERK with its inhibitor PD98059 decreased AGE-induced HUVECs angiogenesis. Furthermore, the inhibition and silencing of Src suppressed the AGE-induced ERK activation. And the silencing of AGEs receptor (RAGE) inhibited the AGE-induced ERK activation and angiogenesis as well. In conclusions, this study demonstrated that Src plays a pivotal role in AGE-promoted HUVECs angiogenesis by phosphorylating ERK, and very likely through RAGE-Src-ERK pathway.
Keywords: ERK; Src; advanced glycation end products; angiogenesis; endothelial cells.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Src in Vascular Hyperpermeability Induced by Advanced Glycation End Products.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 18;5:14090. doi: 10.1038/srep14090. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26381822 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Moesin in Advanced Glycation End Products-Induced Angiogenesis of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells.Sci Rep. 2016 Mar 9;6:22749. doi: 10.1038/srep22749. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 26956714 Free PMC article.
-
The protective effect of Smilax glabra extract on advanced glycation end products-induced endothelial dysfunction in HUVECs via RAGE-ERK1/2-NF-κB pathway.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Aug 8;155(1):785-95. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.06.028. Epub 2014 Jun 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24953033
-
Mdia1 is Crucial for Advanced Glycation End Product-Induced Endothelial Hyperpermeability.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(4):1717-1730. doi: 10.1159/000487780. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29490301
-
Role of moesin, Src, and ROS in advanced glycation end product-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction.Microcirculation. 2017 Apr;24(3). doi: 10.1111/micc.12358. Microcirculation. 2017. PMID: 28129474 Review.
Cited by
-
Peroxisome proliferator‑activated receptor γ alleviates human umbilical vein endothelial cell injury in deep vein thrombosis by blocking endoplasmic reticulum stress.Exp Ther Med. 2024 Aug 1;28(4):385. doi: 10.3892/etm.2024.12674. eCollection 2024 Oct. Exp Ther Med. 2024. PMID: 39161618 Free PMC article.
-
Piperine Attenuates Lithocholic Acid-Stimulated Interleukin-8 by Suppressing Src/EGFR and Reactive Oxygen Species in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Mar 10;11(3):530. doi: 10.3390/antiox11030530. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326180 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Glycation End Products Induce Atherosclerosis via RAGE/TLR4 Signaling Mediated-M1 Macrophage Polarization-Dependent Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Conversion.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Jan 13;2022:9763377. doi: 10.1155/2022/9763377. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35069982 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Traditional Chinese Medicine: Organ Vascular Injury - Volume II.Front Physiol. 2021 Jun 11;12:677858. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.677858. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34177621 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
UM-164, a Dual Inhibitor of c-Src and p38 MAPK, Suppresses Proliferation of Glioma by Reducing YAP Activity.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 29;14(21):5343. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215343. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker M., Robinson S. D., Lechertier T., Barber P. R., Tavora B. (2012). Use of the mouse aortic ring assay to study angiogenesis. Nat. Protoc. 1 89–104. - PubMed
-
- Bjorge J. D., Pang A. S., Funnell M., Chen K. Y., Diaz R., Magliocco A. M., et al. (2011). Simultaneous siRNA targeting of Src and downstream signaling molecules inhibit tumor formation and metastasis of a human model breast cancer cell line. PLoS One 6:e19309. 10.1371/journal.pone.0019309 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

