Mechanisms Underlying the Synergistic Action of Insulin and Growth Hormone on IGF-I and -II Expression in Grass Carp Hepatocytes
- PMID: 29977227
- PMCID: PMC6021495
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00336
Mechanisms Underlying the Synergistic Action of Insulin and Growth Hormone on IGF-I and -II Expression in Grass Carp Hepatocytes
Abstract
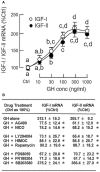
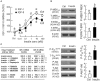
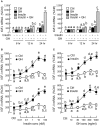
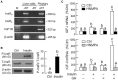
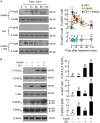
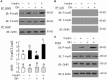
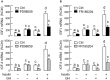
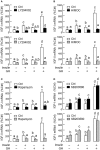
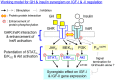
In mammals, insulin is known to modify growth hormone (GH)-induced IGF-I expression at the hepatic level, which also contributes to the functional crosstalk between energy homeostasis and somatotropic axis. However, the studies on the comparative aspects of this phenomenon are limited and the mechanisms involved have not been fully characterized. Using a serum-free culture of grass carp hepatoctyes, the functional interaction between GH and insulin on hepatic expression of IGF-I and -II was examined in a fish model. In carp hepatocytes, GH could up-regulate IGF-I and -II mRNA expression via the JAK2/STAT5, MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways. These stimulatory effects were mimicked by insulin via activation of the PI3K/Akt but not MEK/ERK and P38 MAPK cascades. Although insulin did not activate JAK2 and STAT5 at hepatocyte level, insulin-induced IGF-I and -II mRNA expression were highly dependent on the normal functioning of JAK2/STAT5 pathway. In parallel experiments, insulin co-treatment was found to markedly enhance IGF-I and -II responses induced by GH and these potentiating effects were mediated by insulin receptor (InsR) but not IGF-I receptor. Interestingly, co-treatment with GH also enhanced insulin-induced InsR phosphorylation with a current elevation in protein:protein interaction between GH receptor and phosphorylated InsR and these stimulatory effects were noted with further enhancement in STAT5, ERK1/2 and Akt phosphorylation at hepatocyte level. Consistent with these findings, the potentiating effects of GH and insulin co-treatment on IGF-I and -II mRNA expression were found to be suppressed/abolished by inhibiting JAK2/STAT5, MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt but not P38 MAPK pathways. These results, as a whole, suggest that insulin and GH can act in a synergistic manner in the carp liver to up-regulate IGF-I and -II expression through protein:protein interaction at the receptor level followed by potentiation in post-receptor signaling.
Keywords: grass carp; growth hormone; growth hormone receptor; hepatocytes; insulin; insulin receptor; insulin-like growth factor; signal transduction.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

