Silencing the nosocomial pathogen Serratia marcescens by glyceryl trinitrate
- PMID: 29977251
- PMCID: PMC6016988
- DOI: 10.4314/ahs.v18i1.2
Silencing the nosocomial pathogen Serratia marcescens by glyceryl trinitrate
Abstract
Background: Quorum sensing is a cell-to-cell communication system in bacteria that controls the production of virulence factors. Serratia marcescens is a causative agent of hospital-acquired infections that shows high resistance to antibiotics. This makes the treatment of these infections difficult. Quorum sensing regulates the production of virulence factors of S. marcescens such as prodigiosin, protease, swimming and swarming motilities and formation of biofilms. Inhibition of quorum sensing may be an alternative to antibiotic treatment to avoid emergence of resistance.
Objectives: Testing the ability of glyceryl trinitrate to inhibit quorum sensing and virulence factors of Serratia marcescens.
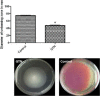
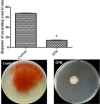
Methods: The inhibiting activities of sub-inhibitory concentration of glyceryl trinitrate against the quorum-sensing regulated violacein pigment in Chromobacterium violaceum CV026 was performed to evaluate the anti-quorum sensing effect of glyceryl trinitrate. The anti-virulence activity was assessed against prodigiosin, protease, biofilm formation in addition to swimming and swarming motilities.
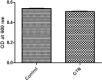
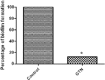
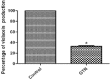
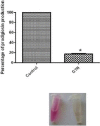
Results: Glyceryl trinitrate at at a concentration of 0.25 mg/ml produced significant inhibitory effects against violacein (67.01%), prodigiosin (82.67%), protease, swimming (36.72%) and swarming (79.31%) motilities and biofilm formation (87.83%).
Conclusion: Glyceryl trinitrate is a quorum sensing and virulence inhibitor that may be useful in treatment of nosocomial infections caused by Serratia marcescens.
Keywords: Serratia marcescens; glyceryl trinitrate; quorum sensing; virulence.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Repurposing anti-diabetic drug "Sitagliptin" as a novel virulence attenuating agent in Serratia marcescens.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 16;15(4):e0231625. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231625. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32298346 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of quorum sensing-mediated virulence in Serratia marcescens by Bacillus subtilis R-18.Microb Pathog. 2018 Jul;120:166-175. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.04.023. Epub 2018 Apr 13. Microb Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29660523
-
Glyceryl trinitrate is a novel inhibitor of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Afr Health Sci. 2016 Dec;16(4):1109-1117. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v16i4.29. Afr Health Sci. 2016. PMID: 28479904 Free PMC article.
-
Serratia marcescens.J Med Microbiol. 1997 Nov;46(11):903-12. doi: 10.1099/00222615-46-11-903. J Med Microbiol. 1997. PMID: 9368530 Review.
-
Genus Carissa L.: a newly explored sustainable source of virulence inhibitors: a mini review.Nat Prod Res. 2025 Mar;39(6):1696-1713. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2024.2385698. Epub 2024 Jul 31. Nat Prod Res. 2025. PMID: 39082374 Review.
Cited by
-
Glyceryl trinitrate blocks staphyloxanthin and biofilm formation in Staphylococcus aureus.Afr Health Sci. 2019 Mar;19(1):1376-1384. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v19i1.10. Afr Health Sci. 2019. PMID: 31148964 Free PMC article.
-
Health issues of concern to Africa and beyond: infections, NCDs and health systems inertia.Afr Health Sci. 2018 Mar;18(1):i-iii. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v18i1.1. Afr Health Sci. 2018. PMID: 29977275 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Relocating Glyceryl Trinitrate as an Anti-Virulence Agent against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Serratia marcescens: Insights from Molecular and In Vivo Investigations.Microorganisms. 2023 Sep 28;11(10):2420. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11102420. Microorganisms. 2023. PMID: 37894078 Free PMC article.
-
Promising FDA-approved drugs with efflux pump inhibitory activities against clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus.PLoS One. 2022 Jul 29;17(7):e0272417. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0272417. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35905077 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hejazi A, Falkiner FR. Serratia marcescens. Journal of Medical Microbiology. 1997;46:903–912. - PubMed
-
- Sarah JC, Neil RW, Abigail KPH, David RS, George PCS. Metabolic and regulatory engineering of Serratia marcescens: mimicking phage-mediated horizontal acquisition of antibiotic biosynthesis and quorum-sensing capacities. Microbiology. 2006;152:1899–1911. - PubMed
-
- Stock I, Burak S, Sherwood KJ, Gruger T, Wiedemann B. Natural anti-microbial susceptibilities of strains of 'unusual’ Serratia species: S. ficaria, S. fonticola, S. odorifera, S. plymuthica and S. rubidaea. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 2003;51:865–885. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
