Low-cost diagnostic test for susceptible and drug-resistant tuberculosis in rural Malawi
- PMID: 29977794
- PMCID: PMC6018377
- DOI: 10.4102/ajlm.v7i1.690
Low-cost diagnostic test for susceptible and drug-resistant tuberculosis in rural Malawi
Abstract
Background: Rural settings where molecular tuberculosis diagnostics are not currently available need easy-to-use tests that do not require additional processing or equipment. While acid-fast bacilli (AFB) smear is the most common and often only tuberculosis diagnosis test performed in rural settings, it is labour intensive, has less-than-ideal sensitivity, and cannot assess tuberculosis drug susceptibility patterns.
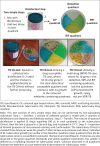
Objective: The objective of this study was to determine the feasibility of a multidrug-resistant (MDR) or extensively drug-resistant (XDR)-tuberculosis coloured agar-based culture test (tuberculosis CX-test), which can detect Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth and evaluate for drug susceptibility to isoniazid, rifampicin and a fluoroquinolone (i.e. ciprofloxacin) in approximately 14 days.
Method: In this study, 101 participants were enrolled who presented to a rural health clinic in central Malawi. They were suspected of having active pulmonary tuberculosis. Participants provided demographic and clinical data and submitted sputum samples for tuberculosis testing using the AFB smear and tuberculosis CX-test.
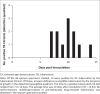
Results: The results showed a high level of concordance between the AFB smear (12 positive) and tuberculosis CX-test (13 positive); only one sample presented discordant results, with the molecular GeneXpert MTB/RIF® test confirming the tuberculosis CX-test results. The average time to a positive tuberculosis CX-test was 10 days. Of the positive samples, the tuberculosis CX-test detected no cases of drug resistance, which was later confirmed by the GeneXpert MTB/RIF®.
Conclusion: These findings demonstrate that the tuberculosis CX-test could be a reliable low-cost diagnostic method for active pulmonary tuberculosis in high tuberculosis burden rural areas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no financial or personal relationships which may have inappropriately influenced them in writing this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the tuberculosis culture color plate test for rapid detection of drug susceptible and drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a resource-limited setting, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2019 May 28;14(5):e0215679. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215679. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31136575 Free PMC article.
-
Use of GeneXpert Mycobacterium tuberculosis/rifampicin for rapid detection of rifampicin resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis strains of clinically suspected multi-drug resistance tuberculosis cases.Ann Transl Med. 2016 May;4(9):168. doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.05.09. Ann Transl Med. 2016. PMID: 27275481 Free PMC article.
-
MDR/XDR-TB Colour Test for drug susceptibility testing of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Northwest Ethiopia.Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Jan;90:213-218. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2019.10.041. Epub 2019 Nov 2. Int J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31689528
-
Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra assays for active tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 27;8(8):CD013359. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013359.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Sep 6;9:CD013359. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013359.pub3. PMID: 32853411 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Xpert Ultra versus Xpert MTB/RIF for pulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults with presumptive pulmonary tuberculosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Feb 22;2(2):CD009593. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009593.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 33616229 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Building resources to meet evolving laboratory medicine challenges in Africa.Afr J Lab Med. 2018 Nov 29;7(1):915. doi: 10.4102/ajlm.v7i1.915. eCollection 2018. Afr J Lab Med. 2018. PMID: 30568895 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Programmatic challenges in managing multidrug-resistant tuberculosis in Malawi.Int J Mycobacteriol. 2021 Jul-Sep;10(3):255-259. doi: 10.4103/ijmy.ijmy_47_21. Int J Mycobacteriol. 2021. PMID: 34494563 Free PMC article.
-
Tuberculosis Phenotypic and Genotypic Drug Susceptibility Testing and Immunodiagnostics: A Review.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 7;13:870768. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.870768. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35874762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the tuberculosis culture color plate test for rapid detection of drug susceptible and drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a resource-limited setting, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2019 May 28;14(5):e0215679. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215679. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31136575 Free PMC article.
-
Collected Thoughts on Mycobacterial Lipoarabinomannan, a Cell Envelope Lipoglycan.Pathogens. 2023 Oct 26;12(11):1281. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12111281. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 38003746 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization 2015 Malawi tuberculosis profile [homepage on the Internet]. c2015 [cited 2017 Jul 10]. Available from: https://extranet.who.int/sree/Reports?op=Replet&name=/WHO_HQ_Reports/G2/...
-
- Cepheid Xpert MTB/RIF [homepage on the Internet]. c2015 [cited 2015 Mar 16]. Available from: http://www.cepheid.com/us/cepheid-solutions/clinical-ivd-tests/critical-...
-
- World Health Organization 2014 Malawi tuberculosis profile. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2014.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Introduction to the core curriculum on tuberculosis: What the clinician should know. Atlanta, GA: CDC Stacks Public Health Publications; 2013, p. 92–94.
-
- Evans CA. GeneXpert--a game-changer for tuberculosis control? PLoS Med. 2011;8:e1001064 https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001064 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources